Motilium
Katie B. Clarkson, M.D. - Greenwood Genetic Center
- Columbia, South Carolina
Trusted motilium 10 mgAn initial hematocrit of 55% within the healthy full-term neonate gradually falls to as low as 30% within the 3-month-old toddler earlier than rising to 35% by 6 months chronic gastritis management motilium 10 mg without prescription. Hemoglobin (Hb) kind can be altering throughout this period: from a 75% concentration of HbF (greater oxygen affinity gastritis diet indian purchase motilium 10mg online, decreased Pao2 gastritis bananas buy motilium 10mg on line, poor tissue unloading) at start to nearly 100% HbA (reduced oxygen affinity uremic gastritis symptoms generic motilium 10 mg without a prescription, excessive Pao2, good tissue unloading) by 6 months. In current years there was increased emphasis on avoiding excessive fluid administration; thus blood loss is now generally replaced by both colloid (eg, albumin) or packed red blood cells. In premature and sick neonates, the target hematocrit (for transfusion) could additionally be as nice as 40%, whereas in healthy older children a hematocrit of 20% to 26% is usually properly tolerated. Because of their small intravascular volume, neonates and infants are at an increased risk for electrolyte disturbances (eg, hyperglycemia, hyperkalemia, and hypocalcemia) that may accompany fast blood transfusion. Platelets and fresh frozen plasma, 10 to 15 mL/kg, ought to be given when blood loss exceeds one to two blood volumes. Recent apply, significantly with blood loss from trauma, favors "earlier" administration of plasma and platelets as a part of an enormous transfusion protocol. One unit of platelets per 10 kg weight raises the platelet rely by about 50,000/L. In latest years some investigators have questioned the very existence of the third space, and a few have asserted that the third space exists as a consequence of extreme fluid administration. One in style fluid administration guideline is zero to 2 mL/kg/h for comparatively atraumatic surgical procedure (eg, strabismus correction where there must be no third-space loss) and as a lot as 6 to 10 mL/kg/h for traumatic procedures (eg, abdominal abscess). It is safe to say that every one issues regarding the third house have by no means been extra controversial. Regional Anesthesia and Analgesia the first makes use of of regional techniques in pediatric anesthesia have been to supplement and scale back general anesthetic requirements and to present higher postoperative ache reduction. Regional blocks in kids (as in adults) are sometimes facilitated by ultrasound steering, generally with nerve stimulation. Caudal blocks have proved helpful following quite lots of surgical procedures, together with circumcision, inguinal herniorrhaphy, hypospadias restore, anal surgery, clubfoot restore, and other subumbilical procedures. Contraindications embody an infection around the sacral hiatus, coagulopathy, or anatomic abnormalities. The patient is often frivolously anesthetized or sedated and positioned within the lateral place. After the attribute pop that alerts penetration of the sacrococcygeal membrane, the needle angle of method is reduced and the needle is advanced only some extra millimeters to keep away from entering the dural sac or the anterior physique of the sacrum. Aspiration is used to check for blood or cerebrospinal fluid; local anesthetic can then be slowly injected; failure of a 2-mL take a look at dose of native anesthetic with epinephrine (1:200,000) to produce tachycardia helps exclude intravascular placement. Ropivacaine seems to have much less cardiac toxicity than bupivacaine compared milligram to milligram. Addition of epinephrine to caudal options tends to enhance the diploma of motor block. Clonidine, both by itself or combined with native anesthetics, has additionally been extensively used. Morphine sulfate (25 mcg/kg) or hydromorphone (6 mcg/kg) may be added to the local anesthetic answer to delay postoperative analgesia for inpatients, but will increase the risk of delayed postoperative respiratory melancholy. The volume of native anesthetic required is dependent upon the extent of blockade desired, starting from 0. Placement of 20-gauge caudal catheters with continuous infusion of native anesthetic (eg, 0. Complications are uncommon however embrace local anesthetic toxicity from elevated blood concentrations (eg, seizures, hypotension, arrhythmias), spinal blockade, and respiratory melancholy. Lumbar and thoracic epidural catheters can be positioned in anesthetized kids using the standard loss-of-resistance technique and both a midline or paramedian method. In young children, caudal epidural catheters have been passed right into a thoracic position with the tip localized radiographically. Spinal anesthesia has been used in some facilities for infraumbilical procedures in neonates and infants. Intravenous access could be established (conveniently in the foot) after the spinal anesthetic has been administered. This method has turn out to be more extensively used for neonates and infants because the potential danger of neurotoxicity from general anesthesia has acquired greater consideration. When the area of operation is the upper extremity, we recommend these brachial plexus procedures that can most readily be performed utilizing ultrasound steerage, specifically axillary, supraclavicular, and infraclavicular blocks. We suggest that interscalene block be carried out in anesthetized sufferers solely by these with expertise and skill with ultrasound steering and just for procedures where other block strategies can be inferior (eg, higher shoulder procedures) because of the reported rare prevalence of unintended intramedullary injections when interscalene blocks were carried out in anesthetized adults. Single-shot and continuous femoral, adductor canal, and sciatic blocks are simply performed in youngsters utilizing ultrasound guidance. A wide number of other terminal nerve blocks (eg, digital nerve, median nerve, occipital nerve, etc) are simply performed to scale back postoperative pain in kids. Sedation for Procedures In & Out of the Operating Room Sedation is commonly requested for pediatric patients inside and out of doors the operating room for nonsurgical procedures. Cooperation and motionlessness could additionally be required for imaging research, bronchoscopy, gastrointestinal endoscopy, cardiac catheterization, dressing modifications, and minor procedures (eg, casting and bone marrow aspiration). Requirements differ relying on the affected person and the process, ranging from anxiolysis (minimal sedation), to conscious sedation (moderate sedation and analgesia), to deep sedation/analgesia, and eventually to general anesthesia. Anesthesiologists are held to the same standards whether they present average or deep sedation or they supply general anesthesia. Airway obstruction and hypoventilation are probably the most commonly encountered issues related to average or deep sedation. With deep sedation and common anesthesia cardiovascular depression can additionally be an issue. One of the sedatives commonly used by nonanesthesia personnel up to now was chloral hydrate, 25 to 100 mg/kg orally or rectally. It has a sluggish onset of up to 60 min and an extended half-life (8�11 h) that results in prolonged somnolence. Although it typically has little effect on ventilation, it can trigger fatal airway obstruction in sufferers with sleep apnea. Doses ought to be decreased whenever a couple of agent is used because of the potential for synergistic respiratory and cardiovascular despair. In nations aside from the United States, propofol is often administered using the Diprifusor, a computercontrolled infusion pump that maintains a relentless goal site focus. Supplemental oxygen and shut monitoring of the airway, ventilation, and different vital signs are necessary (as with different agents). Emergence & Recovery Pediatric patients are significantly vulnerable to two frequent postanesthetic issues: laryngospasm and postintubation croup. Laryngospasm Laryngospasm is a forceful, involuntary spasm of the laryngeal musculature caused by stimulation of the superior laryngeal nerve (see Chapter 19). It may happen at induction, emergence, or any time in between without an endotracheal tube.
Generic motilium 10 mg with visaMaternal deaths are often because of gastritis diet kencing generic 10 mg motilium with mastercard stroke gastritis eating plan 10 mg motilium with amex, pulmonary edema gastritis diet mango discount motilium 10 mg line, hepatic necrosis or rupture gastritis diet 6 weeks buy motilium 10 mg on-line, or a combination of these problems. Pathophysiology & Manifestations the pathophysiology of preeclampsia is related to vascular dysfunction of the placenta, leading to irregular prostaglandin metabolism. Endothelial dysfunction may scale back production of nitric oxide and improve production of endothelin-1. Marked vascular reactivity and endothelial harm scale back placental perfusion and may result in widespread systemic manifestations. Severe preeclampsia considerably increases both maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. Features of severe preeclampsia embrace the standard options of preeclampsia in association with any of the following: blood pressure greater than 160/110 mm Hg, thrombocytopenia (<100,000/L), proteinuria higher than 5 g/d, impaired liver function, progressive kidney insufficiency (serum creatinine focus higher than 1. Patients with severe preeclampsia or eclampsia have broadly differing hemodynamic profiles. Most patients have low-normal cardiac filling pressures with elevated systemic vascular resistance, but cardiac output may be decreased, regular, or elevated. Preeclampsia is normally defined as a systolic blood pressure larger than 140 mm Hg or diastolic strain larger than ninety mm Hg on two occasions a minimum of four h apart after the 20th week of gestation in a lady with beforehand regular blood pressure, accompanied by proteinuria (>300 mg/d) or protein/creatinine ratio higher than 0. Neurological Headache Visual disturbances Hyperexcitability Seizures Intracranial hemorrhage Cerebral edema Pulmonary Upper airway edema Pulmonary edema Cardiovascular Decreased intravascular volume Increased arteriolar resistance Hypertension Heart failure Hepatic Impaired perform Elevated enzymes Hematoma Rupture Renal Proteinuria Sodium retention Decreased glomerular filtration Renal failure Hematological Coagulopathy Thrombocytopenia Platelet dysfunction Prolonged partial thromboplastin time Microangiopathic hemolysis (usually labetalol, 5�10 mg, or hydralazine, 5 mg intravenously), and magnesium sulfate (4 g loading adopted by 1�3 g/h intravenously) to deal with hyperreflexia and prevent convulsions. It is really helpful that corticosteroids be given if the fetus is viable and 33 weeks of gestation or much less. Invasive arterial and central venous monitoring are indicated in sufferers with severe hypertension, pulmonary edema, refractory oliguria, or a combination of those; in such sufferers an intravenous vasodilator infusion may be necessary. Anesthetic Management Standard anesthetic practices could also be used for patients with delicate preeclampsia. Spinal and epidural anesthesia are related to similar decreases in arterial blood stress in these sufferers. Patients with severe disease, nonetheless, are critically sick and require stabilization prior to administration of any anesthetic, together with control of hypertension and correction of hypovolemia. In the absence of coagulopathy, steady epidural anesthesia is the first selection for most patients with preeclampsia throughout labor and vaginal supply. Moreover, steady epidural anesthesia avoids the increased danger of a failed intubation as a end result of extreme edema of the higher airway. A platelet count and coagulation profile ought to be checked prior to the establishment of regional anesthesia in sufferers with severe preeclampsia. It has been really helpful that regional anesthesia be avoided if the platelet count is less than a hundred,000/L, however a platelet depend as little as 50,000/L may be acceptable in selected circumstances, particularly when the depend has been secure and world coagulation, as measured by thrombelastography testing, is regular. Continuous epidural anesthesia decreases catecholamine secretion and improves uteroplacental perfusion by up to 75% in these patients, provided hypotension is prevented. Goal-directed hemodynamic and fluid remedy utilizing arterial pulse wave contour evaluation or other noninvasive cardiac function screens such as echocardiography may be employed to information fluid substitute. Use of an epinephrine-containing test dose for epidural anesthesia is controversial because of questionable reliability (see the earlier part, Prevention of Unintentional Intravascular and Intrathecal Injection) and the danger of exacerbating hypertension. Hypotension should be handled with smaller than traditional doses of vasopressors as a end result of these patients are inclined to be very delicate to these brokers. Therefore, each spinal and epidural anesthetics are cheap choices for cesarean section in a preeclamptic affected person. Intraarterial blood strain monitoring is indicated in patients with extreme hypertension throughout each common and regional anesthesia. The short-term administration of intravenous nicardipine or clevidipine may be used to treat intraoperative hypertension. Because magnesium potentiates muscle relaxants, doses of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants should be reduced in patients receiving magnesium remedy and must be guided by a peripheral nerve stimulator. The affected person with suspected magnesium toxicity, manifested by hyporeflexia, excessive sedation, blurred imaginative and prescient, respiratory compromise, and cardiac despair, may be handled with intravenous administration of calcium gluconate (1 g over 10 min). These sufferers are higher managed with intraspinal opioids alone, systemic medications, pudendal nerve blocks, and, if necessary, general anesthesia. Entry of amniotic fluid into the maternal circulation can occur through any break in the uteroplacental membranes. Such breaks might happen during normal delivery or cesarean section or following placental abruption, placenta previa, or uterine rupture. In addition to the mechanical effects of fetal particles, varied prostaglandins and leukotrienes in amniotic fluid seem to play an important function within the genesis of this syndrome. The alternate term anaphylactoid syndrome of pregnancy has been suggested to emphasize the systemic function of chemical mediators. Patients typically current with sudden tachypnea, cyanosis, shock, and generalized bleeding. Mental standing adjustments, together with seizures, and pulmonary edema might develop; the latter has both cardiogenic and noncardiogenic parts. Although the analysis may be firmly established solely by demonstrating fetal parts in the maternal circulation (usually at autopsy or less commonly by aspirating amniotic fluid from a central venous catheter), amniotic fluid embolism should always be advised by sudden respiratory misery and circulatory collapse. The presentation could initially mimic acute pulmonary thromboembolism, venous air embolism, overwhelming septicemia, or hepatic rupture or cerebral hemorrhage in a patient with toxemia. When cardiac arrest happens previous to supply of the fetus, the efficacy of closed-chest compressions may be marginal at finest. Although most pregnant patients with cardiac illness have rheumatic heart illness, an increasing number of parturients are presenting with corrected or palliated congenital lesions. Anesthetic administration is directed toward using methods that minimize the added stresses of labor and delivery, and particular administration of the varied lesions is discussed elsewhere. Patients in the first group profit from the reduced systemic vascular resistance attributable to neuraxial analgesia and anesthesia strategies, however often not from excessive fluid administration. These sufferers include those with mitral or aortic insufficiency, persistent heart failure, or congenital lesions with left-to-right shunting. The induced sympathectomy from spinal or epidural methods reduces each preload and afterload, relieves pulmonary congestion, and in some instances, increases cardiac output. These patients embody those with aortic stenosis, congenital lesions with right-to-left or bidirectional shunting, or primary pulmonary hypertension. Expeditious delivery appears to improve maternal and fetal consequence, and quick cesarean delivery ought to subsequently be carried out. Once the patient is resuscitated, mechanical air flow, fluid resuscitation, and inotropes are greatest provided under the steerage of invasive hemodynamic monitoring. Uterine atony is handled with oxytocin, methylergonovine, and prostaglandin F2, whereas important coagulopathies are handled with platelets and coagulation factors primarily based on laboratory findings. Early ligation of the inner iliac (hypogastric) arteries might assist keep away from hysterectomy and scale back blood loss. Any compromise of the uteroplacental circulation readily 15 produces fetal asphyxia.
Syndromes - Erosion or decalcification of the bone
- Convulsions
- You notice redness, swelling, or discharge from the area
- Tests that show your baby is not growing well or is not getting enough blood and oxygen
- Increased pressure inside the skull
- Metabolic disturbances
- Burning or stinging feeling in the face
- Ballet
- Fluids by IV
- Slit-lamp ophthalmoscopy: You will sit in a chair with the instrument placed in front of you. You will be asked to rest your chin and forehead on a support to keep your head steady. The health care provider will use the microscope part of the slit lamp and a tiny lens placed close to the front of the eye. The health care provider can see about the same with this technique as with indirect ophthalmoscopy, but with higher magnification.
Buy 10mg motilium mastercardLumbar cerebrospinal fluid drainage for thoracoabdominal aortic surgical procedure: Rationale and practical concerns for administration gastritis symptoms when pregnancy effective motilium 10 mg. Current outcomes of off-pump versus on-pump coronary artery bypass grafting: Evidence from randomized controlled trials gastritis diet in pregnancy buy discount motilium 10 mg on line. Current randomized management trials gastritis symptoms when pregnancy order 10mg motilium otc, observational studies and meta analysis in off-pump coronary surgical procedure gastritis symptoms heartburn discount motilium 10mg visa. Anesthetic pharmacology and perioperative concerns for coronary heart transplantation. The proper mainstem bronchus lies in a more linear association with the trachea, whereas the left mainstem bronchus lies in a extra angular orientation with the trachea. At this volume, the inward elastic recoil of the lung approximates the outward elastic recoil of the chest (including resting diaphragmatic tone). This improve is probably liable for the conventional agerelated decline in arterial O2 rigidity. Local elements are extra essential than the autonomic system in influencing pulmonary vascular tone. The overall impact of shunting is to lower (dilute) arterial O2 content material; this type of shunt is referred to as right-to-left. The generally used inhalation anesthetics rely upon the lungs for uptake and elimination. Both inhalation and intravenously administered anesthetics produce prominent respiratory unwanted effects. Moreover, muscle paralysis, unusual positioning during surgery, and methods such as one-lung anesthesia and cardiopulmonary bypass profoundly alter regular pulmonary physiology. This article reviews the essential pulmonary ideas necessary for understanding and applying anesthetic techniques. Although the pulmonary effects of every of the varied anesthetic agents are mentioned elsewhere in the e-book, this chapter additionally reviews the general results of basic anesthesia on lung function. Rib Cage & Muscles of Respiration the rib cage accommodates the 2 lungs, every surrounded by its own pleura. The apex of the chest is small, permitting only for entry of the trachea, esophagus, and blood vessels, whereas the base is shaped by the diaphragm. Contraction of the diaphragm-the principal pulmonary muscle-causes the bottom of the thoracic cavity to descend 1. Accessory respiratory muscle tissue also enhance chest quantity (and lung expansion) by their action on the ribs. Each rib (except for the last two) articulates posteriorly with a vertebra and is angulated downward because it attaches anteriorly to the sternum. During regular respiratory, the diaphragm, and, to a lesser extent, the external intercostal muscle tissue, are answerable for inspiration; expiration is mostly passive. With rising effort, the sternocleidomastoid, scalene, and pectoralis muscle tissue may be recruited throughout inspiration. The sternocleidomastoid muscle tissue help in elevating the rib cage, whereas the scalene muscle tissue prevent inward displacement of the higher ribs throughout inspiration. Expiration is often passive in the supine place, but becomes active in the upright position and with elevated effort. Exhalation could also be facilitated by the abdominal muscle tissue (rectus abdominis, exterior and inner oblique, and transversus) and perhaps the internal intercostal muscles-aiding the downward movement of the ribs. Although not normally thought of respiratory muscle tissue, some pharyngeal muscular tissues are essential in maintaining the patency of the airway. Tonic and reflex inspiratory exercise within the genioglossus keeps the tongue away from the posterior pharyngeal wall. Tonic activity within the levator palati, tensor palati, palatopharyngeus, and palatoglossus prevents the soft palate from falling again towards the posterior pharynx, significantly in the supine position. The trachea begins on the lower border of the cricoid cartilage, extends to the carina, and has an average size of 10 to thirteen cm. It is composed of C-shaped cartilaginous rings, which form the anterior and lateral partitions of the trachea and are linked posteriorly by the membranous wall of the trachea. The cricoid cartilage is the narrowest a part of the trachea, with a mean diameter of 17 mm in men and 13 mm in ladies. The tracheal lumen narrows slightly because it progresses toward the carina, the place it bifurcates into the best and left mainstem bronchi at the stage of the sternal angle. The proper mainstem bronchus continues as the bronchus intermedius after the take-off of the proper higher lobe bronchus. The distance from the tracheal carina to the takeoff of the right upper lobe bronchus is a median of 2. One in each 250 individuals within the common inhabitants may have an abnormal take-off of the right upper lobe bronchus rising from above the tracheal carina on the proper facet. The left mainstem 1 the trachea serves as a conduit for ventilation bronchus is longer than the right mainstem bronchus and measures a mean of 5. The left mainstem bronchus divides into the left higher lobe bronchus and the left decrease lobe bronchus. Humidification and filtering of impressed air are capabilities of the higher airway (nose, mouth, and pharynx). An estimated 300 to 500 million alveoli provide an enormous membrane surface area (50�100 m2) for gas trade within the average grownup. With every successive division, the mucosa makes a gradual transition from ciliated columnar to cuboidal and at last to flat alveolar epithelium. Gas exchange can occur solely throughout the flat epithelium, which begins to appear on respiratory bronchioles (generations 17�19). The wall of the airway steadily loses its cartilaginous help (at the bronchioles) and then its clean muscle. Loss of cartilaginous assist causes the patency of smaller airways to become dependent on radial traction by the elastic recoil of the surrounding tissue; as a corollary, airway diameter becomes depending on complete lung volume. Cilia on the columnar and cuboidal epithelium normally beat in a synchronized style, such that mucus produced by the secretory glands lining the airway (and any related micro organism or debris) moves toward the mouth. In the upright place, the biggest alveoli are at the pulmonary apex, whereas the smallest are inclined to be on the base. On the skinny facet, the alveolar epithelium and capillary endothelium are separated by their respective mobile and basement membranes; on the thick aspect, where fluid and solute change occurs, the pulmonary interstitial space separates alveolar epithelium from capillary endothelium. The pulmonary interstitial area contains primarily elastin, collagen, and nerve fibers. These tight junctions are necessary in stopping the passage of enormous oncotically active molecules similar to albumin into the alveolus. These inclusions comprise surfactant, an important substance essential for regular pulmonary mechanics. Neutrophils are additionally usually current in smokers and sufferers with pneumonia or acute lung damage. Pulmonary Circulation & Lymphatics the lungs are supplied by two circulations, pulmonary and bronchial. The bronchial circulation arises from the left coronary heart and sustains the metabolic needs of the tracheobronchial tree.
Discount 10 mg motilium with amexThe hypertensive episode in this case may be due to gastritis forum buy 10 mg motilium overnight delivery a previously undiagnosed pheochromocytoma gastritis head symptoms generic motilium 10mg fast delivery. If a number of surgeries are planned gastritis diet ����� cheap 10 mg motilium with visa, pheochromocytoma resection will usually be scheduled first gastritis diet �������������� motilium 10 mg line. Calcitonin is a polypeptide manufactured by the parafollicular cells (C cells) in the thyroid gland. It is secreted in response to will increase in plasma ionic calcium and tends to lower calcium ranges by affecting kidney and bone operate. An extra or deficiency of calcitonin has minor results in people in contrast with the results of parathyroid problems. Because of the life-threatening hemodynamic adjustments associated with pheochromocytoma, this entity must be medically managed earlier than any surgical procedure could be thought of (see Case Discussion, Chapter 14). Workup of the tumor reveals hypercalcemia and an elevated calcitonin degree, which leads to the diagnosis of medullary most cancers of the thyroid and primary hyperparathyroidism. The operation is canceled, an arterial line is inserted, and the patient is treated with intravenous esmolol and nicardipine. Society for Ambulatory Anesthesia Consensus Statement on Selection of Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery. Primary hyperparathyroidism: Review and suggestions on evaluation, analysis, and management. High-dose perioperative corticosteroids in steroidtreated patients present process major colorectal surgical procedure: Necessary or overkill Hypovitaminosis D in hospitalized sufferers: A marker of frailty or a disease requiring remedy Succinylcholine increases intraocular pressure by 5 to 10 mm Hg for 5 to 10 min after administration, principally through prolonged contracture of the extraocular muscle tissue. Traction on extraocular muscular tissues, pressure on the eyeball, administration of a retrobulbar block, and trauma to the eye can elicit all kinds of cardiac arrhythmias starting from bradycardia and ventricular ectopy to sinus arrest or ventricular fibrillation. Complications involving the intraocular growth of gas bubbles injected by the ophthalmologist could be averted by discontinuing nitrous oxide at least 15 min previous to the injection of air or sulfur hexafluoride, or by avoiding using nitrous oxide totally. Medications utilized topically to mucosa are absorbed systemically at a fee intermediate between absorption following intravenous and subcutaneous injection. Echothiophate is an irreversible cholinesterase inhibitor used within the remedy of glaucoma. Because succinylcholine is metabolized by this enzyme, echothiophate will extend its period of motion. The key to inducing anesthesia in a affected person with an open eye damage is controlling intraocular strain with a clean induction. Coughing and gagging during intubation is averted by first attaining a deep level of anesthesia and profound paralysis. The postretrobulbar block apnea syndrome might be because of injection of native anesthetic into the optic nerve sheath, with spread into the cerebrospinal fluid. Regardless of the anesthetic approach, American Society of Anesthesiologists standards for basic monitoring should be employed, and tools and medicines needed for airway administration and resuscitation should be immediately obtainable. Mastery of common and sedation anesthesia techniques for ophthalmic surgical procedure and an intensive understanding of probably complicating issues- together with the comorbidities of an rising geriatric affected person population-are needed for optimum perioperative outcomes. In addition, nearly all of ophthalmic procedures are carried out beneath topical or regional anesthesia. The anesthesiologist have to be conversant in their potential complications, including those of the accompanying sedation, even when not personally administering the topical anesthetic or the block. If the contents of the sphere enhance, the normal intraocular pressure of 12 to 20 mm Hg will rise. Similarly, intraocular strain will rise if the amount of blood inside the globe is increased. A rise in venous stress will enhance intraocular pressure by decreasing aqueous drainage and increasing choroidal blood volume. Any event that alters arterial blood strain or ventilation (eg, laryngoscopy, intubation, airway obstruction, coughing, Trendelenburg position) can even have an effect on intraocular stress (Table 36�1). Alternatively, compressing the globe with no proportional change within the volume of its contents will enhance intraocular stress. Pressure on the eye from a malpositioned mask, improper inclined positioning, or retrobulbar hemorrhage can result in a marked enhance in intraocular stress, attainable eye pain, and momentary or permanent visible changes. Intraocular stress helps to maintain the form and the optical properties of the attention. For example, blinking raises intraocular stress by 5 mm Hg, and squinting (forced contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscles) might transiently increase intraocular stress greater than 50 mm Hg. However, even brief episodes of increased intraocular stress in sufferers with underlying low ophthalmic artery pressure (eg, from systemic hypotension, arteriosclerotic involvement of the retinal artery) could trigger retinal ischemia. When the globe is opened by surgical incision (Table 36�2) or traumatic perforation, intraocular stress approaches atmospheric stress. Any fac1 tor that will increase intraocular pressure within the setting of an open globe might cause drainage of aqueous or extrusion of vitreous by way of the wound, critical complications that may permanently worsen vision. Intraocular pressure decreases with inhalational anesthetics in proportion to anesthetic depth. Topically administered anticholinergic medicine result in pupillary dilation (mydriasis), which can precipitate or worsen angle-closure glaucoma. However, in studies of lots of of patients with open eye accidents, no affected person experienced extrusion of ocular contents after administration of succinylcholine. Nevertheless, dogma usually trumps knowledge and ophthalmic surgeons may request that it not be administered in sure circumstances. Unlike other skeletal muscle, extraocular muscles include myocytes with a number of neuromuscular junctions, and depolarization of those cells by succinylcholine causes prolonged contracture. The oculocardiac reflex is mostly encountered in kids undergoing strabismus surgery, though it can be evoked in all age teams and through a selection of ocular procedures. Routine prophylaxis for the oculocardiac reflex is controversial, particularly in adults. Anticholinergic medication is usually useful in preventing the oculocardiac reflex, and intravenous atropine or glycopyrrolate instantly previous to surgical procedure is more effective than intramuscular premedication. However, anticholinergic treatment must be administered with caution to any patient who has, or may have, coronary artery illness, due to the potential for improve in coronary heart fee adequate to induce myocardial ischemia. Retrobulbar blockade or deep inhalational anesthesia can also be of worth in preempting the oculocardiac reflex, although administration of a retrobulbar block could itself initiate the oculocardiac reflex. Management of the oculocardiac reflex includes (1) immediate notification of the surgeon and cessation of surgical stimulation till heart rate will increase; (2) affirmation of enough ventilation, oxygenation, and depth of anesthesia; (3) administration of intravenous atropine (10 mcg/kg) if bradycardia persists; and (4) in recalcitrant episodes, infiltration of the rectus muscles with native anesthetic. Intravitreal air injection will are inclined to flatten a indifferent retina and facilitate anatomically right healing.
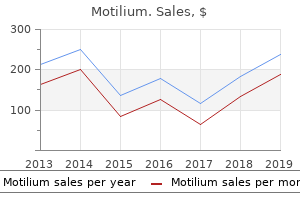
Motilium: 10 mg
Generic motilium 10mg with amexAs previously famous chronic gastritis zinc order 10mg motilium amex, compound A gastritis symptoms in infants order motilium 10 mg fast delivery, a breakdown product of sevoflurane gastritis cystica profunda definition motilium 10mg cheap, causes acute kidney injury in laboratory animals chronic gastritis frequently leads to order motilium 10 mg on line. Low fresh gas move charges promote its accumulation within the anesthesia machine respiration circuit. Ketamine minimally impacts kidney function and may, relative to other anesthetic agents, preserve kidney perform throughout hemorrhagic hypovolemia. Drugs with antidopaminergic activity-such as metoclopramide, phenothiazines, and droperidol- may impair the renal response to dopamine. Mechanisms of harm include vasoconstriction, direct tubular injury, drug-induced immunological and inflammatory responses, and renal microvascular or tubular obstruction. Pneumoperitoneum produced during laparoscopy creates an stomach compartment syndrome�like state. Intraabdominal hypertension and stomach compartment syndrome: An underappreciated cause of acute kidney damage. The majority of diuretics exert their action on the luminal cell membrane from within the renal tubules. Because practically all diuretics are extremely protein sure, relatively little of the free drug enters the tubules by filtration. Most diuretics should subsequently be secreted by the proximal tubule (usually via the natural anion pump) to exert their action. Impaired delivery into the renal tubules accounts for resistance to diuretics in sufferers with decreased kidney function. Their presence within the proximal tubule limits passive water reabsorption that usually follows energetic sodium reabsorption. Although their main effect is to improve water excretion, in giant doses, osmotically energetic diuretics also increase electrolyte excretion. The similar mechanism also impairs water and solute reabsorption in the loop of Henle. Mannitol activates intrarenal synthesis of vasodilating prostaglandins and could additionally be a free radical scavenger. Prophylaxis Against Acute Kidney Injury in High-Risk Patients Many clinicians continue to administer mannitol for kidney protection and, less frequently, to convert oliguric acute kidney failure to nonoliguric kidney failure, with the goal of reducing associated morbidity and mortality. In addition, high-dose mannitol could be nephrotoxic, especially in patients with impaired kidney operate. Sodium reabsorption at that web site requires that all four sites on the Na+�K+�2Cl� luminal provider protein be occupied. The large quantities of Na+ and Cl� presented to the distal nephron overwhelm its restricted reabsorptive capability. A marked increase in diuresis might happen when a loop diuretic is combined with a thiazide diuretic, particularly metolazone (Mykrox, Zaroxolyn, Zytanix). Evaluation of Acute Oliguria Mannitol will augment urinary output within the setting of hypovolemia but could have little impact in the presence of extreme glomerular or tubular damage. The optimum preliminary strategy to analysis of acute oliguria is to correct hypovolemia and optimize cardiac output and kidney perfusion. Acute Reduction of Intraocular Pressure in the Perioperative Period See Chapter 36. Side Effects Mannitol solutions are hypertonic and acutely raise plasma and extracellular osmolality. A speedy intracellular to extracellular shift of water can transiently enhance intravascular quantity and precipitate cardiac decompensation and pulmonary edema in sufferers with limited cardiac reserve. Transient hyponatremia and reductions in hemoglobin concentration are also frequent and symbolize acute hemodilution resulting from fast motion of water out of cells; a small and transient increase in plasma potassium concentration can also be noticed. As previously noted, high-dose mannitol could be nephrotoxic, especially in sufferers with impaired kidney function. Edematous States (Sodium Overload) these issues include heart failure, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, and renal insufficiency. When given intravenously, these loop diuretics can quickly reverse cardiac and pulmonary manifestations of fluid overload. Hypertension Loop diuretics could additionally be used as adjuncts to different hypotensive agents, significantly when thiazides alone are ineffective (see later discussion). Evaluation of Acute Oliguria the optimal preliminary strategy to acute oliguria is to appropriate hypovolemia and optimize cardiac output and renal perfusion. Intravenous Dosages the intravenous doses are furosemide, 10 to one hundred mg; bumetanide, 0. These diuretics act at the distal tubule, together with the connecting phase, and inhibition of sodium reabsorption at this site impairs diluting however not concentrating capability. When given alone, thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics increase Na+ excretion to solely 3% to 5% of the filtered load due to enhanced compensatory Na+ reabsorption within the accumulating tubules. In distinction to their effects on sodium excretion, thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics augment Ca2+ reabsorption in the distal tubule. Indapamide has some vasodilating properties and is the one thiazide or thiazide-like diuretic with important hepatic excretion. Side Effects Increased supply of Na+ to the distal and collecting tubules will increase K+ and H+ secretion at these websites and thus produce hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis. Marked Na+ losses will also lead to hypovolemia and prerenal azotemia; secondary hyperaldosteronism typically accentuates the hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis. Urinary calcium and magnesium loss promoted by loop diuretics might result in hypocalcemia or hypomagnesemia, or each. Hyperuricemia may end result from increased urate reabsorption and from competitive inhibition of urate secretion within the proximal tubule. Reversible and irreversible listening to loss has been reported with loop diuretics, particularly furosemide and ethacrynic acid. Hypertension Thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics are sometimes chosen as first-line agents within the treatment of hypertension (see Chapter 21), and so they have been shown to improve long-term outcomes on this disorder. Edematous Disorders (Sodium Overload) these drugs are used to deal with mild to average edema and congestive coronary heart failure related to delicate to average sodium overload. Hypercalciuria Thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics are often used to lower calcium excretion in sufferers who form calcium-containing kidney stones. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus the efficacy of those agents on this dysfunction is based upon their capability to impair diluting capability and improve urine osmolality (see Chapter 49). Potassiumsparing diuretics inhibit Na+ reabsorption within the accumulating tubules and therefore can maximally excrete only 1% to 2% of the filtered Na+ load. They are often used along side more potent diuretics for their potassium-sparing effect. Uses In sufferers with hypertension, these agents are sometimes combined with a thiazide or similar diuretic to decrease hypokalemia produced by the other agent. They have been added to more potent loop diuretics in congestive heart failure patients with marked potassium wasting. Aldosterone Antagonists (Spironolactone & Eplerenone) Spironolactone (Aldactone) and eplerenone (Inspra) are direct antagonists of accumulating tubule aldosterone receptor.
Discount motilium 10mg onlineA comparison of epidural analgesia with combined continuous femoral-sciatic nerve blocks after total knee replacement gastritis upper gi purchase 10mg motilium mastercard. Cervical spine harm is presumed in any trauma affected person presenting with neck ache or any suggestion of neurologic damage in addition to those with lack of consciousness gastritis gerd buy motilium 10mg low price, vital head harm and/or intoxication gastritis dietz discount motilium 10mg otc. In the affected person with blunt or penetrating injury gastritis zungenbelag cheap 10mg motilium mastercard, providers ought to maintain a excessive degree of suspicion for pulmonary harm that might evolve right into a rigidity pneumothorax when mechanical air flow is initiated. No trauma patient should die with out having potential pressure pneumothorax relieved. Damage management surgery is a surgical intervention intended to stop hemorrhage and limit gastrointestinal contamination of the abdominal compartment in severely injured and bleeding sufferers. An emergent exploratory laparotomy is carried out in a start�stop trend, making an attempt to discover and control bleeding accidents, while affording the anesthesia provider opportunities for resuscitation and stopping prolonged hypotension and hypothermia between surgical interventions. Cardiac output declines abruptly by up to 50% inside 30 minutes of damage because of massive vasoconstriction, inducing a state of normovolemic hypoperfusion (burn shock). A progressive decrease in trauma survivability is first seen beginning round age 50. Significant underlying medical situations contribute to elevated trauma-related morbidity and mortality after even modest injuries. Trauma is a quantity one cause of morbidity and mortality in all age groups and a number one explanation for demise in each the young (under 20 years old) and aged (over 70 years old). All elements of trauma care, from that offered on the scene, via transport, resuscitation, surgical procedure, intensive care, and rehabilitation, have to be coordinated if trauma sufferers are to have the greatest opportunity for full restoration. The development of criteria for Level 1 Trauma Centers has additionally improved trauma care by directing severely injured patients to services with appropriate trauma care resources. Although trauma anesthesia is usually regarded as a novel matter, many of the rules for managing trauma patients are relevant to any unstable or hemorrhaging patient. Thus, many common points encountered in typical anesthesia follow are addressed on this chapter. This pattern also implies that when referred to as upon for assistance in airway management in the emergency division, anesthesia providers must expect a challenging airway since routine airway administration techniques have likely proved unsuccessful. There are three necessary features of airway management within the initial analysis of a trauma patient: (1) the necessity for basic life support intervention; (2) the presumed presence of a cervical spinal wire damage till confirmed otherwise; and (3) the potential for failed endotracheal intubation. In those with persistent unresponsiveness, efficient basic life help expertise enhance preoxygenation and cut back the risk for hypoxia throughout 1 airway administration interventions. All trauma patients ought to be presumed to have a full abdomen and thereby be at elevated danger of pulmonary aspiration. Cervical collar ("C-collar") software before transport protects the cervical spinal cord by limiting cervical extension, and firstresponders should utilize well-designed "hard" collars (eg, Aspen, Miami-J, Philadelphia) for cervical backbone stabilization. Traditional "soft" cervical collars provide primarily no useful cervical backbone stabilization. Hard collar cervical backbone stabilization negatively impacts positioning for direct laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation, and alternative airway management units (eg, video laryngoscope, fiberoptic bronchoscope) should be instantly available. If tracheal intubation is required, the entrance part of the C-collar could be eliminated so long as the head and neck are maintained in neutral place by a chosen assistant sustaining handbook inline stabilization. Alternative supraglottic devices for airway management (eg, King supralaryngeal device) may be used if direct laryngoscopy has failed in any environment (prehospital to intensive care unit). The extended presence of supraglottic devices in the airway has been related to tongue engorgement resulting from the massive, proximal cuff obstructing venous outflow from the tongue, and in some circumstances, tongue engorgement has been sufficiently extreme to warrant tracheostomy prior to its removal. Limited proof exists that prehospital airway administration in trauma patients improves outcomes. However, failed endotracheal intubation within the prehospital surroundings certainly exposes patients to important morbidity. Failed intubation attempts typically result in systemic hypoxemia, and repeated hypoxemic events after even modest neurological injury additional exacerbate the preliminary neurological insult (the second hit phenomenon). Cricothyroidotomies and tracheostomies are rarely required for securing trauma airways. However, when trauma significantly alters or distorts the facial or higher airway anatomy to the purpose of preventing efficient masks ventilation, or when hemorrhage into the airway precludes the affected person from mendacity supine, elective cricothyroidotomy or tracheostomy should be considered before any attempts are made at sedating or paralyzing the affected person for oral intubation. The glottic opening lies between the large cuff positioned at the base of the tongue and the smaller balloon positioned within the proximal esophagus. Peak inspiratory pressure and tidal volumes must be monitored throughout the preliminary resuscitation. Abrupt cardiovascular collapse shortly after instituting mechanical air flow could signal the presence of a pneumothorax. Any traumarelated cardiovascular collapse is managed by disconnecting the patient from mechanical air flow and performing bilateral needle thoracostomies. This intervention is achieved by inserting a 14-gauge intravenous catheter into the second intercostal area in the midclavicular line followed by bigger, more practical thoracostomy tube insertion placed in the midaxillary line. Circulation Signs of a pulse and blood pressure are sought during the main trauma patient survey. The absence of a pulse following trauma is associated with dismal possibilities of survival. An emergent ultrasound analysis of the chest and abdomen is indicated for any patient arriving after trauma in cardiac arrest, as is bilateral needle chest decompression. The ultrasound evaluation will concentrate on the presence of an empty heart or huge blood collections in the chest or stomach, which are indications of deadly damage. The American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma not endorses the utilization of emergency thoracotomy in treating sufferers with out blood pressure or palpable pulse following blunt trauma, given the dearth of evidence supporting survival following this intervention. In victims of penetrating trauma without a palpable pulse or blood pressure, however with organized cardiac rhythm, a resuscitative thoracotomy may supply some survivability however mortality remains exceedingly excessive. Any extremity with important vascular damage ought to have a tourniquet applied on the earliest attainable moment ("stop the bleed"). The fear of tourniquet-induced limb ischemia usually distracts first responders from making prompt, effective interventions in controlling hemorrhage with a tourniquet. Hemorrhage, not limb ischemia and limb perform, is essentially the most pressing menace to life, and it should be controlled by any efficient measure at the earliest possible opportunity. Level of consciousness, pupillary dimension and reaction, lateralizing indicators suggesting intracranial or extracranial accidents, and indications of potential spinal wire damage are rapidly evaluated. Additional causes of depressed neurological perform (eg, alcohol/drug intoxication, results of illicit or prescribed drugs, hypoglycemia, hypoperfusion, brain or spinal wire injury) must even be addressed. Mechanisms of damage have to be thought-about as nicely as exclusion of different elements in figuring out the danger for central nervous system trauma. Persistently depressed levels of consciousness should be thought-about a result of central nervous system injury till disproved by emergent diagnostic research (eg, computed tomography scan). Patients with free fluid in these areas, as properly as two of the following-penetrating damage, systolic blood pressures lower than 90 mm Hg, or heart rate over one hundred twenty beats per minute-are prone to have a excessive mortality, trauma-induced coagulopathy, and require an enormous transfusion. These critical findings have been validated in quite a few trauma studies and warrant instant surgical intervention for hemorrhage management.
Eugenia Caryophyllata (Clove). Motilium. - Are there safety concerns?
- How does Clove work?
- What is Clove?
- Dosing considerations for Clove.
- Toothache, "dry socket" following tooth extraction, vomiting, upset stomach, nausea, gas (flatulence), diarrhea, hernia, mouth and throat swelling (inflammation), cough, and other conditions.
- Premature ejaculation when applied directly to the skin of the penis in combination with other medicines.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96275
Discount 10mg motilium with visaOnce the venous line is completely occluded and systolic arterial stress is judged to be enough (>80�90 mm Hg) gastritis symptoms in cats buy motilium 10mg line, pump flow is stopped and the affected person is evaluated chronic gastritis omeprazole buy 10 mg motilium visa. Some surgeons wean by clamping the venous line after which progressively "filling" the patient with arterial influx gastritis diet ������� discount motilium 10 mg on-line. Hypovolemic sufferers include these with normal ventricular function and those with varying levels of impairment gastritis hiatal hernia diet purchase motilium 10mg on line. Those with preserved myocardial perform rapidly reply to infusion of blood through the aortic cannula. Blood strain and cardiac output rise with every bolus, and the increase turns into progressively extra sustained. Most of those sufferers keep good blood stress and cardiac output with a left ventricular filling stress under 10 to 15 mm Hg. The patient must be evaluated for unrecognized ischemia (kinked graft or coronary vasospasm), valvular dysfunction, shunting, or proper ventricular failure (the distention is primarily right sided). The balloon should inflate just after the dicrotic notch is seen on the intraaortic strain tracing to augment diastolic blood pressure and coronary circulate after closure of the aortic valve. Ideally the balloon, which is positioned in the descending aorta just distal to the left subclavian artery, ought to inflate on the dicrotic notch (1) and be utterly deflated just because the left ventricle begins to eject (2). Note the decrease end-diastolic pressures after balloon augmentation and slightly decrease systolic pressure in the following beat. Balloon deflation must be timed just previous to left ventricular ejection to decrease its afterload. Early deflation makes diastolic augmentation and afterload reduction much less efficient. If myocardial gorgeous is a significant contributor or there are areas of hibernating myocardium, a delayed enchancment in contractile operate may enable complete weaning from all medicine and help units solely after 12 to 48 h of therapy. The routine use of calcium equally could worsen ischemic harm and will contribute to coronary spasm (particularly in sufferers who had been taking calcium channel blockers preoperatively). Epinephrine is essentially the most potent inotrope and is usually efficient in increasing each cardiac output and systemic blood stress when others agents have failed. On the other hand, dopamine is usually more practical in rising blood stress than in growing cardiac output. Interestingly, when infused to increase cardiac output to comparable extents, epinephrine is related to no extra improve (and maybe less) in coronary heart price than dobutamine. Inamrinone, enoximone, milrinone, and olprinone are selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors, and inotropes with arterial and venous dilator properties. The combination of an inodilator (usually milrinone) and a -adrenergic agonist ends in at least additive (and presumably synergistic) inotropic effects. Some clinicians use norepinephrine together with phosphodiesterase inhibitors to stop extreme reductions in systemic arterial pressure. There are experimental stories in which doses of methylene blue or vitamin C have successfully counteracted vasodilation that could not be overcome with norepinephrine, vasopressin, or each. Drug Clevidipine Fenoldopam Nicardipine Nitric oxide Nitroglycerin Nitroprusside Prostaglandin E1 Dosage 1�16 mg/h zero. Ventricular arrhythmias in this setting can quickly deteriorate into ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation. Reversal of Anticoagulation Once hemostasis is judged acceptable and the affected person continues to stay steady, heparin activity is reversed with protamine. Protamine is a highly positively charged protein that binds and successfully inactivates heparin (a extremely negatively charged polysaccharide). A still less complicated approach is to give adult sufferers a defined dose (eg, 3�4 mg/kg) then check for adequacy of reversal. Automated heparin�protamine titration assays successfully measure residual heparin focus and can also be used to calculate the protamine dose. The justification for using this technique is the observation that when protamine is given in excess it might have anticoagulant exercise, though this has by no means been demonstrated in humans. This method additionally assumes that administered protamine remains in circulation for a protracted time (which has been proven false in research of sufferers undergoing cardiac surgery). To accomplish the heparin:protamine titration, premeasured quantities of protamine are added in varying portions to a quantity of wells, every containing a blood sample. The well whose protamine concentration finest matches the heparin focus will clot first. Clotting will be prolonged in wells containing both too much or too little protamine. The protamine dose can then be estimated by multiplying the focus within the tube that clots oxide has the added benefit of not reducing systemic arterial stress. Systolic arterial pressure is usually maintained at less than one hundred forty mm Hg to decrease bleeding. Checking for bleeding, notably from the posterior floor of the heart, requires lifting the heart, which might trigger durations of precipitous hypotension. Some surgeons might want to be told of the extent and length of the hypotension; others have higher situational consciousness. The atrial cannula(s) is removed earlier than the aortic cannula in case the latter should be used to quickly administer quantity to the affected person. Catastrophic protamine reactions usually embrace myocardial depression and marked pulmonary hypertension. Persistent Bleeding 13 Persistent bleeding usually follows extended durations of bypass (>2 h) and in most instances has multiple causes. Inadequate surgical control of bleeding websites, incomplete reversal of heparin, thrombocytopenia, platelet dysfunction, hypothermia-induced coagulation defects, and undiagnosed preoperative hemostatic defects, or newly acquired issue deficiency or hypofibrinogenemia may be accountable. Reheparinization (heparin rebound) after obvious adequate reversal is poorly understood but usually attributed to redistribution of peripherally sure heparin to the central compartment and to the exceedingly short persistence of protamine in blood. Hypofibrinogenemia (fibrinogen stage <100 mg/dL or a prolonged thrombin time with out residual heparin) ought to be handled with cryoprecipitate. Fenoldopam could also be used and has the added benefit of accelerating renal blood flow, which might possibly improve kidney perform in the early postoperative period. Portable monitoring equipment, infusion pumps, and a full oxygen cylinder with a self-inflating bag for ventilation ought to be readied prior to the end of the operation. A spare endotracheal tube, laryngoscope, succinylcholine, and emergency resuscitation medicine also needs to accompany the affected person. Many centers insist on a regular protocol for the "handoff," and we strongly advocate this apply. The emphasis within the first few postoperative hours ought to be on sustaining hemodynamic stability and monitoring for extreme postoperative 14 bleeding. Chest tube drainage in the first 2 h of more than 250 to 300 mL/h (10 mL/kg/h)-in the absence of a hemostatic defect-is extreme and should require surgical reexploration. Hypertension despite analgesia and sedation is a common postoperative downside and may usually be handled promptly in order not to exacerbate bleeding or myocardial ischemia. Nitroprusside, nitroglycerin, clevidipine, nicardipine, or esmolol is usually used. Fluid substitute may be guided by filling pressures, echocardiography, or by responses to treatment. Most sufferers present with relative hypovolemia for several hours following operation.
Proven 10mg motiliumPatients without chronic hepatitis B or C infection often have a positive response to immunosuppressants and are handled with long-term corticosteroid remedy with or without azathioprine gastritis gagging cheap 10 mg motilium overnight delivery. Anesthetic Management Patients with persistent persistent or continual lobular hepatitis ought to be handled equally to those with acute hepatitis gastritis diet sweet potato generic 10mg motilium fast delivery. In distinction gastritis best diet buy 10mg motilium with amex, these with continual active hepatitis must be assumed to already have cirrhosis and must be handled accordingly (as discussed next) gastritis symptoms list motilium 10mg low price. Patients can often be categorised as having one of three distinct syndromes primarily based on a liver biopsy: chronic persistent hepatitis, persistent lobular Cirrhosis the liver of irritation, hepatocellular damage, and the resulting fibrosis and regeneration of hepatocytes. Other causes embrace continual lively hepatitis (postnecrotic cirrhosis), chronic biliary inflammation or obstruction (primary biliary cirrhosis, sclerosing cholangitis), persistent right-sided congestive coronary heart failure (cardiac cirrhosis), autoimmune hepatitis, hemochromatosis, Wilson disease, 1-antitrypsin deficiency, and cryptogenic cirrhosis. Regardless of the cause, hepatocyte necrosis is followed by fibrosis 5 and nodular regeneration. Manifestations are usually absent initially, however jaundice and ascites finally develop in most patients. Other indicators embrace spider angiomas, palmar erythema, gynecomastia, and splenomegaly. Moreover, cirrhosis is generally related to the event of three major issues: (1) variceal hemorrhage from portal hypertension, (2) intractable fluid retention within the form of ascites and the hepatorenal syndrome, and (3) hepatic encephalopathy or coma. Approximately 10% of patients with cirrhosis additionally develop a minimum of one episode of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and some patients eventually develop hepatocellular carcinoma. A few ailments can produce hepatic fibrosis without hepatocellular necrosis or nodular regeneration, leading to portal hypertension and its associated problems with hepatocellular operate typically preserved. These problems embody schistosomiasis, idiopathic portal fibrosis (Banti syndrome), and congenital hepatic fibrosis. Obstruction of the hepatic veins or inferior vena cava (Budd�Chiari syndrome) also can cause portal hypertension. The latter could additionally be the end result of venous thrombosis (hypercoagulable state), a tumor thrombus (eg, renal carcinoma), or occlusive illness of the sublobular hepatic veins. Preoperative Considerations the detrimental effects of anesthesia and surgery on hepatic blood circulate are discussed later in this section. Patients with cirrhosis are at increased danger of degradation of liver perform due to limited functional reserve. Successful anesthetic management of these patients relies on recognizing the multisystem nature of cirrhosis (Table 34�3) and controlling or preventing its issues. Gastrointestinal Manifestations Portal hypertension leads to the development of in depth portosystemic venous collateral channels. Four major collateral sites are generally acknowledged: gastroesophageal, hemorrhoidal, periumbilical, and retroperitoneal. Portal hypertension is often obvious preoperatively, as evidenced by dilated abdomi6 nal wall veins (caput medusae). Massive bleeding from gastroesophageal varices is a serious explanation for morbidity and mortality in sufferers with liver illness, and, in addition to the results of acute blood loss, the absorbed nitrogen load from the breakdown of blood within the gastrointestinal tract can precipitate hepatic encephalopathy. The remedy of variceal bleeding is primarily supportive, however frequently entails endoscopic procedures for identification of the bleeding site(s) and therapeutic maneuvers, corresponding to injection sclerosis of varices, monopolar and bipolar electrocoagulation, or utility of hemoclips or bands. Endoscopic unipolar electrocautery may adversely affect implanted cardiac pacing and defibrillator units. Nonoperative therapy contains vasopressin, somatostatin, propranolol, and balloon tamponade with a Sengstaken�Blakemore tube. High doses of vasopressin can lead to congestive heart failure or myocardial ischemia; concomitant infusion of intravenous nitroglycerin could reduce the likelihood of those problems and bleeding. Perioperative danger correlates with degree of hepatic impairment, based mostly on scientific and laboratory findings. Shunting procedures are usually performed on low-risk patients, whereas ablative surgical procedure, esophageal transection, and gastric devascularization are reserved for high-risk sufferers. Hematologic Manifestations Anemia, thrombocytopenia, and, less commonly, leukopenia may be current. The explanation for the anemia is usually multifactorial and consists of blood loss, elevated pink blood cell destruction, bone marrow suppression, and dietary deficiencies. Congestive splenomegaly secondary to portal hypertension is basically answerable for the thrombocytopenia and leukopenia. Enhanced fibrinolysis secondary to decreased clearance of activators of the fibrinolytic system may also contribute to the coagulopathy. Protein breakdown from extreme blood transfusions can precipitate encephalopathy. Clotting elements must be changed with applicable blood products, such as fresh frozen plasma and cryoprecipitate. Platelet transfusions ought to be thought-about immediately previous to surgery for platelet counts lower than 75,000/L. Assessment of integrity of the coagulation system by viscoelastic expertise will provide particular management information. Increased cardiac output Increased coronary heart rate Decreased systemic vascular resistance Increased circulating volume Coronary artery illness Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy (often unrecognized) Low systemic vascular resistance conceals poor left ventricular function Reduced responsiveness to -agonists C. Circulatory Manifestations End-stage liver disease, and in particular, cirrhosis of the liver may be associated with disorders of all main organ methods (Tables 34�3 and 34�5). Cardiovascular changes noticed in cirrhotic sufferers 7 are usually these of a hyperdynamic circulation, although clinically important cirrhotic cardiomyopathy is usually present and not recognized (Table 34�6). There could also be a reduced cardiac contractile response to stress, altered diastolic relaxation, downregulation of -adrenergic receptors, and electrophysiological modifications on account of cirrhotic cardiomyopathy. Echocardiographic examination of cardiac function might initially be interpreted as normal because of significant afterload reduction caused by low systemic vascular resistance. Noninvasive stress imaging is frequently used to assess coronary artery illness in patients older than age 50 years and in these with cardiac risk factors. Intrapulmonary vascular dilation causes intrapulmonary right-to-left shunting and an increase in the alveolar-to-arterial oxygen gradient. Increased pulmonary vascular resistance: vasoconstriction, structural vascular transforming, and eventual fibrosis Mean pulmonary artery strain >25 mm Hg with normal pulmonary capillary wedge strain Right ventricular overload Right coronary heart failure Hepatic congestion Increased liver transplantation mortality threat, especially if imply pulmonary artery pressure is >35 mm Hg clean muscle proliferation, vasoconstriction, intimal proliferation, and eventual fibrosis, all presenting as obstruction causing an elevated resistance to pulmonary blood circulate. In some patients, pulmonary hypertension will reverse shortly after transplant; however, other patients may require months or years of ongoing vasodilator therapy. Respiratory Manifestations Disturbances in pulmonary fuel exchange and ventilatory mechanics are sometimes current. As beforehand famous, hypoxemia is frequently present and is due to right-to-left shunting of as a lot as 40% of cardiac output. Shunting is because of a rise in each pulmonary arteriovenous communications (absolute) and ventilation/perfusion mismatching (relative). Moreover, massive quantities of ascites produce a restrictive ventilatory defect that increases the work of respiratory. Review of the chest radiograph and arterial blood gasoline measurements is beneficial preoperatively because atelectasis and hypoxemia are often not evident on scientific examination.
Discount motilium 10mg lineThe sedation can be additional augmented by extra small dosages of fentanyl gastritis diet en espanol trusted 10 mg motilium, midazolam erythematous gastritis definition order motilium 10 mg overnight delivery, or propofol gastritis pronounce buy motilium 10 mg line. Incremental doses of propofol gastritis diet foods eat safe 10 mg motilium, 20 to 30 mg for adults, are sometimes used if the surgeon requires a brief episode of deep sedation or general anesthesia. These strategies require a high level of cooperation and participation by each the surgeon and anesthesia supplier. Immediately afterward, his respirations seem labored with a loud inspiratory stridor. The acute onset of inspiratory stridor in a postoperative patient may be because of laryngospasm, laryngeal edema, overseas body aspiration, or vocal wire dysfunction. Laryngospasm, an involuntary spasm of the laryngeal musculature, could additionally be triggered by blood or secretions stimulating the superior laryngeal nerve (see Chapter 19). Laryngeal edema could additionally be caused by an allergic drug response, hereditary or iatrogenic angioedema, or a traumatic intubation. Vocal twine dysfunction might be because of residual muscle relaxant impact, hypocalcemic alkalotic tetany, intubation trauma, or paradoxical vocal wire motion. Immediate measures that should be considered embody raising the top of the mattress to lower venous and arterial pressures on the website of bleeding and aggressively treating any degree of systolic hypertension with intravenous antihypertensive agents. Despite these measures, the bleeding continues, and surgical intervention seems to be essential. Before induction of general anesthesia in a bleeding affected person, hypovolemia must be corrected with isotonic crystalloid or with colloid. The diploma of hypovolemia could additionally be troublesome to assess as a outcome of much of the blood may be swallowed, but it can be estimated by adjustments in vital indicators, postural hypotension, and hematocrit. Cross-matched blood should be available, and a second large-bore intravenous line secured. It should be appreciated that from an anesthetic standpoint, that is an entirely totally different affected person than the one who introduced for surgical procedure initially: the affected person now has a full stomach, is hypovolemic, and could additionally be harder to intubate. Induction drug alternative (eg, ketamine, etomidate) and dosage should anticipate the potential for hypotension from persistent hypovolemia. Qualified personnel and acceptable tools for an emergency tracheostomy must be immediately out there. The arterial provide of the nose is provided by the inner maxillary artery and the anterior ethmoid artery. Rigid bronchoscopy in airway overseas bodies: Value of the medical and radiological signs. The position of cricothyrotomy, tracheostomy, and percutaneous tracheostomy in airway management. Anaesthesia for head and neck surgery: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines. Integration of a troublesome airway response group into a hospital emergency response system. Emergent awake tracheostomy�The five-year experience at an city tertiary care middle. Can submandibular tracheal intubation be a substitute for tracheotomy during surgical procedure for main maxiollofacial fractures Perioperative management of antithrombotic remedy in frequent otolaryngologic surgical procedures: State of the artwork evaluation. The laryngeal masks airway for pediatric adenotonsillectomy: Predictors of failure and complications. Effects of hypotensive anesthesia on reducing intraoperative blood loss, duration of operation, and quality of surgical area during orthognathic surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Superficial or deep cervical plexus block for carotid endarterectomy: A systematic review of issues. An replace on the perioperative administration of kids with upper respiratory tract infections. Complications and 30-day hospital readmission rates of patients present process tracheostomy: A prospective analysis. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of the laryngeal nerves throughout anterior neck surgery: A evaluate. Anaesthetic considerations for sufferers receiving photodynamic remedy in head and neck surgical procedure. Use of a pneumatic tourniquet on an extremity creates a bloodless subject that greatly facilitates surgery. Fat embolism syndrome classically presents inside 72 h following long-bone or pelvic fracture, with the triad of dyspnea, confusion, and petechiae. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism may cause morbidity and mortality following orthopedic operations on the pelvis and lower extremities. Flexion and extension lateral radiographs of the cervical spine ought to be obtained preoperatively in sufferers with rheumatoid arthritis severe sufficient to require steroids, immune remedy, or methotrexate. Effective communication between the anesthesia provider and surgeon is essential throughout bilateral hip arthroplasty. Interscalene brachial plexus block with or and not using a perineural catheter is ideally fitted to shoulder procedures. Patients might current as neonates with congenital limb deformities, as youngsters with sports-related accidents, as adults for procedures ranging from excision of minor soft-tissue mass to joint alternative, or at any age with bone most cancers. This article focuses on perioperative care issues particular to sufferers present process widespread orthopedic surgical procedures. For instance, patients with lengthy bone fractures are predisposed to fats embolism syndrome. Patients are at elevated threat for venous thromboembolism following pelvic, hip, and knee operations. Perioperative care of patients present process cervical, thoracic, and lumbar backbone procedures is reviewed in Chapter 27. Neuraxial and different regional anesthetic strategies play an essential role in decreasing the incidence of perioperative thromboembolic complications, providing postoperative analgesia, and facilitating early rehabilitation and hospital discharge. Advances in surgical strategies, such as minimally invasive approaches to knee and hip alternative, are necessitating modifications in anesthetic and perioperative administration to facilitate in a single day and even same-day discharge of sufferers who formerly required days of hospitalization. It is impossible to cowl the anesthetic implications of diverse orthopedic operations in a single chapter; therefore, the major focus right here is on perioperative administration issues and strategies for the anesthetic management of sufferers undergoing choose orthopedic surgical procedures. Mixing polymerized methylmethacrylate powder with liquid methylmethacrylate monomer causes polymerization and cross-linking of the polymer chains. This exothermic reaction results in hardening of the cement and expansion against the prosthetic components. The resultant intramedullary hypertension (>500 mm Hg) could cause embolization of fats, bone marrow, cement, and air into venous channels.
Purchase motilium 10 mg with amexInspection and palpation of the again can reveal surgical scars gastritis pepto bismol order 10mg motilium otc, scoliosis chronic superficial gastritis diet cheap motilium 10mg on line, skin lesions gastritis information buy motilium 10mg low cost, and whether or not the spinous processes could be identified gastritis diet ������ buy motilium 10 mg free shipping. Neuraxial anesthesia within the presence of sepsis or bacteremia may theoretically predispose patients to hematogenous unfold of the infectious agents into the epidural or subarachnoid house. Patients with preexisting neurological deficits or demyelinating illnesses could report worsening signs following a neuraxial block. It may be impossible to discern effects or complications of the block from preexisting deficits or unrelated exacerbation of preexisting illness. For these reasons, some riskaverse practitioners argue in opposition to neuraxial anesthesia in such patients. In a retrospective research inspecting the data of 567 sufferers with preexisting neuropathies, 2 of the patients developed new or worsening neuropathy following neuraxial anesthesia. Although this discovering signifies a comparatively low danger of additional injury, examine investigators counsel that an injured nerve is weak to additional harm, increasing the chance of poor neurological outcomes. However, a history of preexisting neurological deficits or demyelinating illness is at greatest a relative contraindication, and the stability of perioperative dangers on this affected person inhabitants could favor neuraxial anesthesia in certain choose sufferers. This could additionally be tough or inconceivable for patients with dementia, psychosis, or emotional instability. Unsedated young children is probably not suitable for pure regional strategies; nevertheless, regional anesthesia is incessantly used with basic anesthesia in youngsters. Fortunately, the incidence of epidural hematoma is reported to be rare (1 in 150,000 epidurals). The use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications continues to increase, inserting an ever-larger variety of patients at potential risk of epidural hematomas. Oral Anticoagulants If neuraxial anesthesia is to be utilized in patients receiving warfarin therapy, a standard prothrombin time and international normalized ratio normally shall be documented prior to the block, until the drug has been discontinued for weeks. However, relying upon affected person factors two half-life intervals is probably not enough to mitigate the increased risk of bleeding following neuraxial procedures. A period from drug discontinuation of up to 5 to six drug halflife intervals may be essential to keep away from elevated bleeding threat. Likewise, issue Xa inhibitors could be assessed by way of assays of factor Xa inhibition. It has been instructed that new oral anticoagulants may be resumed 24 to forty eight h following a neuraxial procedure or removal of an epidural catheter. In distinction, stronger brokers ought to be stopped, and neuraxial blockade should generally be administered solely after their results have worn off. Neuraxial techniques should be prevented in sufferers receiving antiplatelet medications until platelet perform has been recovered. Metabolites of clopidogrel and prasugrel block the P2Y12 receptor, impeding platelet aggregation. Both prasugrel and ticagrelor have larger platelet inhibition in contrast with clopidogrel. Removal of an epidural catheter ought to occur 1 h previous to, or four h following, subsequent heparin dosing. Neuraxial anesthesia must be averted in patients on therapeutic doses of intravenous heparin and with increased partial thromboplastin time. If the affected person is began on heparin after the position of an epidural catheter, the catheter ought to be eliminated only after discontinuation or interruption of heparin infusion and evaluation of the coagulation standing. Prompt prognosis and evacuation of symptomatic epidural hematomas enhance the chance that neuronal perform might be preserved. Supplemental oxygen by way of a face mask or nasal cannula could also be required to keep away from hypoxemia when sedation is used. Minimum monitoring requirements embody blood strain and pulse oximetry for labor analgesia. Monitoring for blocks rendered in surgical anesthesia is the same as that normally anesthesia. Surface Anatomy Spinous processes are normally palpable and assist to outline the midline. Therefore, when performing a lumbar or cervical epidural block (with maximum spinal flexion), the needle is directed with solely a slight cephalad angle, if in any respect, whereas for a thoracic block, the needle have to be angled significantly extra cephalad to enter the thoracic epidural area. In the cervical space, the primary palpable spinous process is that of C2, but the most prominent one is that of C7 (vertebra prominens). Counting spinous processes up or down from these reference points identifies different spinal ranges. A line connecting the posterior superior iliac spine crosses the S2 posterior foramina. In slender individuals, the sacrum is definitely palpable, and the sacral hiatus is felt as a despair just above or between the gluteal clefts and above the coccyx, defining the purpose of entry for caudal blocks. Should lumbar neuraxial anesthesia, when used at the facet of basic anesthesia, be performed after induction of general anesthesia The main arguments for having the affected person asleep are that (1) most patients, if given a choice, would favor to be asleep, and (2) the potential for sudden affected person motion causing injury is markedly diminished. The main argument in favor of neuraxial blockade administration only whereas the affected person is still awake is that the affected person can alert the clinician to paresthesias and pain on injection on this circumstance, each of which have been related to postoperative neurological deficits. Pediatric neuraxial blocks, particularly caudal and epidural blocks, are normally carried out under basic anesthesia. Technical Considerations Neuraxial blocks have to be performed solely in a facility by which all of the tools and medicines wanted for intubation, resuscitation, and common anesthesia are instantly obtainable. Note the target space (interlaminar foramen) for neuraxial blocks increases in dimension with flexion. Patients lie on their side with their knees flexed and pulled high against the stomach or chest, assuming a "fetal place. The melancholy between the spinous processes of the vertebrae above and under the level to be used is palpated; this will be the needle entry website. After the preparation solution has dried, a pores and skin wheal is raised at the degree of the chosen interspace with native anesthetic using a small (25-gauge) needle. Note once more the assistant serving to to provide maximal needle will be directed barely cephalad. The needle additionally feels extra firmly implanted within the back (like "an arrow in a goal"). If bone is contacted superficially, a midline needle is in all probability going hitting the decrease spinous process. As the needle penetrates the ligamentum flavum, an obvious improve in resistance is encountered. Many clinicians routinely use the paramedian strategy for thoracic epidural puncture. After pores and skin preparation and sterile draping (as beforehand described), the skin wheal for a paramedian approach is raised 2 cm lateral to the inferior side of the superior spinous means of the desired stage. Because this approach is lateral to many of the interspinous ligaments and penetrates the paraspinous muscle tissue, the needle might encounter little resistance initially and will not seem to be in firm tissue.
References - Martin DM, Goldman JA, Gilliam J, Nasrallah SM. Goldinduced eosinophilic enterocolitis: response to oral cromolyn sodium. Gastroenterology 1981;80:1567.
- Aytac IA, McKinlay JB, Krane RJ: The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences, BJU Int 84:50n56, 1999.
- Danzl DF, Pozos RS: Accidental hypothermia, N Engl J Med 331:1756-1760, 1994.
- Nitti VW, Tu LM, Gitlin J: Diagnosing bladder outlet obstruction in women, J Urol 161:1535n1540, 1999.
- Dombek MF, Lamm BM, Saltrick K, Mendicino RW, Catanzariti AR. Peroneal tendon tears: a retrospective review. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2003 42(5):250-258.
- Blackburn W: Aorta, coarctation, infantile type. In: Buyse ML (ed): Birth Defects Encyclopedia. Dover, Blackwell Scientific, 1990, pp 157-158.
- Masuda EM, Kistner RL: Long-term results of venous valve reconstruction: a four- to twenty-one-year follow-up, J Vasc Surg 19(3):391-403, 1994.
- Sin DD, Anthonisen NR, Soriano JB, et al. Mortality in COPD: role of comorbidities. Eur Respir J 2006; 28: 1245-1257.
|