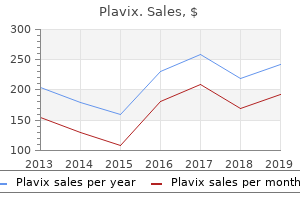
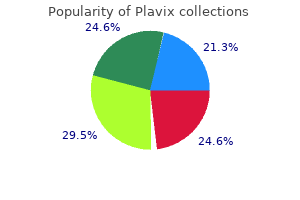
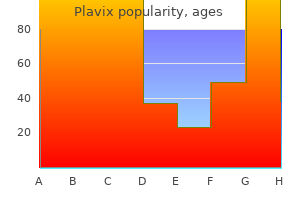
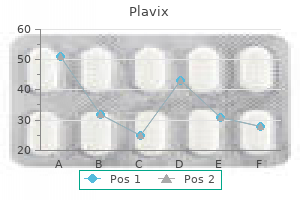
Plavix
Linda Anderson, M.D. - Department of Internal Medicine
- Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Section
- University of Nebraska Medical Center
- Omaha, NE
Plavix: 75 mg
Generic 75mg plavix mastercardHowever heart attack at 25 cheap 75 mg plavix overnight delivery, some studies have lower blood pressure quickly naturally buy 75mg plavix fast delivery, in fact blood pressure log excel plavix 75 mg on-line, indicated enchancment in -cell function by coaching in these patients [40 arrhythmia update 2014 cheap plavix 75 mg,109]. In a study using stimulation with hyperglycemic clamping and arginine bolus, increases in -cell responses were seen in sufferers, who previous to coaching had a moderate residual -cell operate, whereas no change was seen in sufferers with a low remaining secretory capability [109]. One attainable explanation could be that a diminished glucose stress resulting from a rise in target tissue insulin sensitivity could improve the secretory capability of overloaded, yet recoverable, cells. However, in the talked about hyperglycemic clamp study no change in insulin sensitivity and HbA1c was seen. Also in that study other mechanisms than decreased glycemia apparently accounted for the optimistic -cell adaptation to training [152]. The impression of the training-induced diversifications in each secretion and effect of insulin on glucose homeostasis during strange living situations has been evaluated in a study in which sort 2 diabetic patients had blood samples drawn across the clock. Areas underneath plasma focus versus time curves have been similar for glucose whereas energy consumption was no less than as excessive when in comparison with earlier than coaching [109]. Integrated insulin and C-peptide levels were reduced after coaching indicating that during physiologic situations insulin action is enhanced and insulin secretion spared by training [109]. The lack of change in built-in glucose levels is in accordance with the truth that a major change in HbA1c focus is commonly not seen in coaching research. A single bout of extended dynamic train reduces postprandial chylomicron triglyceridemia in type 2 diabetics. The underlying mechanism is a training-induced increase in insulin sensitivity which is accompanied by beneficial relief of overloaded cells and diminished plasma insulin levels. Adding to the danger discount, training additionally tends to favorably influence body fats [158], arterial blood stress [159,160], baroreflex sensitivity [161], endothelium-dependent vasodilation in each conduit and resistance vessels [134,162], skin blood flow [163], the heart rate Ч blood pressure product at rest and during train [158], hypertriglyceridemia and fibrinolysis [159,a hundred and sixty,164], and has antioxidant and anti inflammatory results [165]. In line with these findings, cohort research have in fact proven that in sort 2 diabetic sufferers cardiovascular morbidity and mortality differ inversely with both physical health and stage of bodily exercise and could also be 50% decrease in bodily lively in contrast with sedentary individuals [4,6,166]. Furthermore, both epidemiologic prospective and retrospective studies indicate that regular bodily activity in kind 1 diabetics does protect in opposition to macrovascular in addition to microvascular issues and will increase life expectancy [5,7,168]. In both kinds of diabetes, extra confirmed advantages of normal physical activity are maintenance or enchancment of 602 Chapter 41 cardio train capability and muscle power and, accordingly, a better tolerance in course of bodily calls for. Another benefit that has been proven in wholesome subjects and which in all probability also applies to diabetics is safety towards osteoporosis. Hypoglycemia may even develop many hours after train, as a outcome of enhancement of insulin sensitivity and replenishment of glycogen stores from plasma glucose could last more than 12 hours [170,171]. This means that explicit caution has to be exerted when train is carried out within the night. To meet these challenges the diabetic has to be in good metabolic management previous to exercise [121,131]. Furthermore, the patient must imitate the conventional response to exercise by reducing the insulin dose and/or rising carbohydrate intake (Tables 41. The necessary changes depend upon the train taken, the environment, and the individual, and, accordingly, have to be individually tailored primarily based on frequent blood glucose measurements before, during, and after exercise. The short-acting monomeric insulin analogues are absorbed faster than common insulin and, accordingly, the risk of undesirable interaction between peak insulin concentrations and train is over sooner after a meal if analogues are used compared with common insulin [172,173]. The optimum insulin dosage is dependent upon the depth and period of train and the more energy is spent the less insulin is needed [149]. In response to short-term strenuous exercise, transient hyperglycemia may develop in properly managed type 1 diabetic sufferers [87]. If the ambient temperature is high much less insulin ought to be injected previous to train because absorption from the skin could also be facilitated [174]. Neither on this nor in different situations can exercise-induced hypoglycemia be averted by changing the insulin injection website [174]. Reductions in short-acting insulin dosage taken before exercise might amount to 3080%, and postexercise reductions can also be needed, for instance to avoid nocturnal hypoglycemia [174,175]. Similarly, in order to perform long-term bodily activity, sufferers treated with pump therapy could need to cut back the premeal insulin bolus by more than 50% and even to cease the basal infusion fee while exercising and to cut back it 25% for several hours afterwards [176,177]. On the other hand, a essential discount in insulin dosage prior to less intensive train could lead to a larger enhance in plasma glucose concentrations when a meal is taken after train than on non-exercise days when the total insulin dose is administered [40]. Accordingly, supplemental short-acting insulin could additionally be required, notably if food consumption is elevated after train. It can also be recommended that during exercise classes of reasonable depth lasting greater than 30 min, 1525 g extra readily absorbable carbohydrate must be taken by adult diabetics every 30 min [18]. Carbohydrate may be supplemented by a hundred mL 58% sucrose resolution every 10 min, whereby exercise-induced fluid losses are additionally substituted. After prolonged exhaustive train 100200 g further carbohydrate could also be needed to optimize glycogen repletion and forestall late hypoglycemia [121,178]. Prevention of hypoglycemia by carbohydrate administration before, throughout, and after exercise may be more sensible, significantly in youth, than adjustment of insulin dose, because actions could additionally be spontaneous and of unforeseeable depth and period [79]. The total amount of carbohydrate ingested ought to match the carbohydrate expenditure [84], and tables exist with estimates of carbohydrate utilization throughout varied activities in children of varied body plenty [79]. Although frank hypoglycemia is rare, in sufferers treated with oral hypoglycemic brokers, antidiabetic medication, extent of train, and food consumption ought to, in principle, also be mutually adjusted [72]. Because weight loss often is desirable in these sufferers carbohydrate supplement is much less expedient. Insulin Reduce dose of short-acting (maybe also of intermediate- or long-acting) insulin earlier than exercise. If the affected person has coronary artery disease he or she should, just as any nondiabetic patient, have an echocardiographic examination and a supervised graded exercise check with electrocardiographic and blood pressure monitoring (Table 41. During the take a look at the edge for potential improvement of ischemia, arrhythmia, left ventricular failure or anginal equivalents. Exercise programs at intensities below the crucial threshold can then be prescribed. For instance, in sufferers with angina, cardio training should be carried out at a heart fee a minimum of 10 beats per min decrease than the ischemic threshold. Cardiac illness may be current in sufferers with diabetes within the absence of coronary artery disease. On the opposite hand, the increase in arterial blood strain in response to exercise could also be exaggerated in diabetics [179,182] and, in particular, in hypertensive diabetics [183]. So, in hypertensive diabetics the blood pressure response to train should be monitored initially, and changes in remedy ought to be made accordingly. Autonomic neuropathy is related to elevated mortality from myocardial infarction and sudden death, and it may be a marker for clinically unrecognized cardiac illness [179]. Also diabetic cardiomyopathy with impaired left ventricular operate at rest and through exercise is intently associated with cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy [186]. Because of the risk of an opposed cardiovascular event throughout train, a supervised graded train take a look at is recommended previous to initiation of coaching programs in diabetics with autonomic neuropathy [131,187]. It should all the time be remembered that because of impaired heart price response, in these patients price of perceived exertion is a safer guide for exercise depth than heart rate [187].
Discount 75mg plavix overnight deliveryCareful real-time modulation of window and ranges is sometimes wanted to display the ducts nicely blood pressure pulse rate trusted 75mg plavix. Unfortunately excretion of the biliary contrast material is very variable and is usually poor when serum bilirubin is elevated blood pressure healthy numbers purchase plavix 75 mg on-line. Thin-section imaging arteria humeral discount plavix 75mg on line, as with single-shot quick spin-echo or three-dimensional respiration-triggered turbo spin-echo imaging with parallel imaging allows for detailed cross-sectional interrogation of the biliary tract blood pressure medication that does not lower heart rate cheap plavix 75mg without prescription. Stones and pneumobilia appears as dark-signal filling defects on T2-weighted pictures. T2-weighted images could also be reformatted into thick-section three-dimensional displays. T1-weighted fat-saturation gradient-echo imaging with intravenous gadolinium contrast helps to identify abnormal wall enhancement of the bile duct or hepaticopancreatic parenchymal lesions. Hepatobiliary gadolinium distinction material can also be injected intravenously and, after a period of delay, is excreted into the biliary tract. Hepatobiliary contrast material appears as bright sign within the biliary tract on delayed-phase T1-weighted imaging. Typically a 20-minute delay is sufficient for gadoxetate and a 45- to 120-minute delay for gadobenate dimeglumine to opacify the biliary tract. Bright background liver parenchymal enhancement may restrict the visualization of small intrahepatic bile ducts. Fluoroscopic Imaging Fluoroscopic imaging of the biliary tract could additionally be obtained by both endoscopic retrograde cholangiography, which requires canalization of the bile duct by use of an endoscope, or by percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography, which entails puncture of the biliary tract by inserting a needle or catheter via the pores and skin and into the liver. Fluoroscopic imaging offers the very best in-plane spatial decision of all the imaging modalities and likewise allows for interventions corresponding to mechanical stone extraction or dilatation and drainage of obstructed bile ducts. These imaging methods typically require conscious sedation or common anesthesia. Careful examination of the images for filling defects is required as a end result of only two-dimensional projections are offered. Only the contrast-opacified segments of the bile ducts are seen with fluoroscopic imaging. The intrahepatic ducts (arrowhead) are barely visible as hypodense tubes parallel to the intrahepatic portal veins. These "invisible" nonopacified ducts could outcome from some ducts being oriented in a nondependent location at the time of imaging, however obstruction of the ducts can also be a consideration. However, inference and cautious observation is needed to establish obstructed or in any other case nonopacified bile ducts. In explicit, the best posterior duct might insert immediately onto the frequent hepatic, the left hepatic, or even the cystic duct. Variant cystic ducts could insert medial to the common bile duct or be within a common sheath that also encases the widespread hepatic duct. A common bile duct variant can also run parallel for a protracted distance to the primary pancreatic duct in the pancreatic head. Demographic and Clinical Features Recognition of bile duct variants is important for preoperative planning, as for liver resection or living associated liver transplantation, treating biliary injury, and cholecystectomy. Less common variants are a trifurcation sample where the right anterior, proper posterior, and left ducts converge to inside 5 mm of each other or insertion of the right posterior duct into the cystic duct. Small branches of the best bile duct may insert immediately into the gallbladder. But when hepatectomy is considered, data of bile duct variants is helps to prevent surgical complications. The most necessary consideration is for surgical partial hepatectomy, which can be carried out for resection of tumor such as metastases or cholangiocarcinoma or for liver retrieval in dwelling related liver donation. Surgery is tougher and extra likely to result in problems when two or extra duct anastomoses must be carried out than when just one is required. This variant could result in inadvertent ligation of the frequent bile duct rather than the cystic duct at laparoscopic cholecystectomy. This is a traditional variant but may be essential to acknowledge prior to liver surgical procedure so that the surgeon can plan appropriately for potential surgical bile duct rerouting. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiogram shows the cystic duct (arrowheads) inserting low and medial to the widespread bile duct (arrow). This anatomic variant can be related to a typical sheath that contains the cystic and common bile ducts and may lead to obstruction of the common bile duct when a gallstone is lodged in the cystic duct. An increasingly recognized and regarding variant of the widespread bile duct is the place the pancreatic duct and customary bile duct type a standard channel for more than 1. This variant regularly happens with choledochal cysts and can predispose sufferers to develop cholangiocarcinoma. This variant might predispose stones in both the frequent bile duct or pancreatic duct to trigger obstruction of the adjacent duct. Imaging Findings the identification of bile duct branching variants requires good imaging technique and vigilant image evaluation. None of the imaging modalities is ideal for consistent identification of these variants. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography reveals the best posterior duct (arrow) inserting directly onto the common hepatic duct (arrowhead). This is a standard variant but may be essential to acknowledge previous to liver surgical procedure in order that the surgeon can plan appropriately for potential needed bile duct rerouting. Management/Clinical Issues When liver resection is a attainable treatment, biliary anatomic variants should be sought and reported. Key Points Bile duct anatomic variants are frequent, significantly involving the right posterior bile duct, and may affect surgical method. When stakes are excessive, dedicated imaging of the bile ducts with biliary excreted contrast materials might help to establish biliary and cystic duct variants. Coronal T2-weighted single-shot picture exhibits the common bile duct (arrow) with a long segment in a parallel course with the pancreatic duct (arrowhead) in the pancreatic head. Findings from these studies should ideally be compared with cross-sectional imaging to verify that the complete biliary tract, and particularly the proper posterior bile duct, is opacified. The right posterior bile duct typically drains the posterior and inferior proper lobe of the liver. Confident delineation of branch anatomy in circumstances where the ducts are of normal caliber, as after trauma or in healthy living potential liver donors, could also be challenging. Use of parallel imaging respiratory gated thin-section three-dimensional imaging and probably using hepatobiliary brokers might help to improve the visualization of first- and second-order bile duct branch anatomy. Care ought to be taken to examine areas of obstruction since obstructions may obscure the bile duct department points and trigger ambiguity as to whether a bile duct anatomic variant is current and whether or not surgery would require multiple bile duct anastomoses. For nondilated nonobstructed bile ducts, T1-weighted thin-section imaging with a hepatobiliary agent can additionally be obtained to help enhance confidence within the biliary anatomy. Choledochal Cysts Definition A choledochal cyst is congenital dilatation of the extrahepatic bile duct. The dilatation may involve the intrahepatic ducts and cystic duct in some patients. Demographic and Clinical Features Choledochal cysts have a prevalence of approximately 1 in one hundred,000 people in western international locations and a better prevalence in Asia.
Generic 75mg plavix amexDifferential Diagnosis Bowel perforation: Extravasation of oral contrast material could also be difficult to differentiate from active extravasation of intravenous distinction material hypertension risk factors buy 75mg plavix overnight delivery. Intravenous extravasation is usually of diminished attenuation and increases in dimension on a delayed part as the distinction diffuses away from the location of active hemorrhage blood pressure for stroke purchase 75 mg plavix fast delivery. Delayed enhancement of ascites: Commonly happens after prior intravenous distinction administration and could also be current up to arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease buy 75 mg plavix overnight delivery 3 days after contrast administration blood pressure medication interactions cheap plavix 75mg otc. This is assumed to be due to elevated vascular permeability and is more generally seen in patients with impaired renal function. Management/Clinical Issues Acute intraperitoneal hemorrhage is an emergency often requiring that the affected person be stabilized. On the late portal venous section, the active extravasation increases in measurement and adjustments configuration (arrow in B). Subacute hemorrhage incorporates methemoglobin, which is hyperintense on T1-weighted pictures and initially darkish on T2-weighted photographs but becomes bright on T2-weighted images when purple blood cells lyse. Levy Definition Inflammation of the peritoneum, or peritonitis, may be attributable to infectious or noninfectious inflammatory etiologies. Demographic and Clinical Features Peritonitis might occur in any age group and patient population. On physical examination sufferers with diffuse peritoneal inflammation have belly tenderness and may have guarding or rebound tenderness. Bacterial peritonitis could happen in sufferers with bowel perforation, indwelling catheters, spontaneously in patients with ascites, or as a postoperative traumatic complication. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis occurs in sufferers with persistent ascites and is probably the most generally occurring form of bacterial peritonitis. The term granulomatous peritonitis is used when granulomas kind as a outcome of the inflammatory course of. Tuberculosis, histoplasmosis, and Pneumocystis pneumoniae infection may cause a granulomatous peritonitis, as can overseas material similar to talc and barium, meconium, bowel contents, the contents of ruptured ovarian cysts, bile, or gallstones within the peritoneal cavity. Sclerosing encapsulating peritonitis is a uncommon persistent inflammatory disorder of the peritoneum that happens mostly in patients undergoing chronic peritoneal dialysis. It may also be idiopathic, related to ventriculoperitoneal shunts, liver transplantation, tuberculosis, overseas material, and as a uncommon complication of beta-blocker remedy. Pathology Grossly, purulent material is found on the peritoneal surfaces in generalized peritonitis due to bowel perforations. Granulomatous peritonitis is characterized by nodular thickening of the peritoneal surfaces. At histology the granulomata of tuberculosis characteristically have caseation with central necrosis rimmed by histiocytes and occasional lymphocytes. If the affected person has accompanying ascites, tuberculosis organisms can sometimes be cultured from the ascitic fluid. Imaging Features the imaging findings of bacterial peritonitis vary relying on the purpose for the peritonitis. In bowel perforation, findings in lots of instances are associated to the etiology of the perforation, pneumoperitoneum, and localized abscess formation. Patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis normally have a big quantity of ascites from chronic liver illness and portal hypertension. Tuberculous peritonitis has been described as having three imaging patterns (wet, fibrotic fastened, and dry plastic), relying on the relative quantity of ascites and gentle tissue. Although tuberculous ascites characteristically has high attenuation, it may even have water attenuation. Soft tissue masses or nodules studding the peritoneal surfaces or infiltrating the omentum and mesenteries in all forms symbolize caseous nodules and fibrosis. Concomitant lymph node enlargement within the peripancreatic and periportal areas, mesenteries, or retroperitoneum can also be present. The imaging features of peritoneal histoplasmosis are indistinguishable from tuberculosis. Linear calcifications might develop in the mesenteries and omenta as the illness progresses. Differential Diagnosis Loculated ascites: Ascites loculated by adhesions or inflammatory processes could simulate loculated fluid collections and abscess. Cystic or cystic-appearing metastases: Mucinous metastasis from pseudomyxoma peritonei or mucinous carcinomatosis is of low attenuation and may be mistaken for ascites. Mucinous metastases could additionally be located in the nondependent portion of the peritoneal cavity and exhibit mass effect on intraperitoneal organs, similar to scalloping of their peritoneal surfaces. Management/Clinical Issues All forms of peritonitis, together with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, are often troublesome to deal with and require longterm antibiotic therapy. Ultrasound-guided paracentesis may be required to get hold of ascitic fluid for Gram stain and tradition. Key Points Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis occurs in patients with persistent ascites and is the most commonly occurring form of bacterial peritonitis. In tuberculous peritonitis, soft tissue masses or nodules studding the peritoneal surfaces or infiltrating the omentum and mesenteries represent caseation and fibrosis. Imaging options of encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis in steady ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. Lymphangioma Definition Abdominal lymphangiomas are unusual developmental lesions of vascular origin. Lesions with massive cystic locules are sometimes referred to as cystic hygromas, cystic lymphangiomas, or cavernous lymphangiomas. Imaging Features the overwhelming majority of intra-abdominal lymphangiomas are located in the small bowel mesentery. They may also occur in the retroperitoneum or inside intraperitoneal and retroperitoneal organs and bowel. On ultrasound the walls and internal septations of lymphangiomas are echogenic and may include detectable arterial and venous blood circulate on spectral and colour Doppler. Demographic and Clinical Features Lymphangiomas are mostly found in the pediatric inhabitants. Most lymphangiomas (95%) occur in the head and neck area and have a childhood presentation. The remaining 5% are located within the mesentery, retroperitoneum, belly viscera, and mediastinum. Patients with mesenteric lymphangiomas could present with stomach pain, rising abdominal girth, a palpable mass, and indicators and signs of bowel obstruction, or they might be asymptomatic with a cystic mesenteric mass discovered incidentally. Mesenteric lymphangiomas may also be a part of a uncommon systemic disorder of lymphatic proliferation referred to as lymphangiomatosis, which includes multiple anatomic websites. Fluid-filled bowel loops have an analogous appearance to the lymphangioma however they comprise folds.
Purchase 75 mg plavix free shippingSince then blood pressure medication lipitor cheap plavix 75mg without prescription, numerous studies have proven that increased hexosamine flux can induce insulin resistance in cultured cells and whole animals (reviewed in [42]) hypertension of the eye 75 mg plavix fast delivery. Specifically: · overexpression in muscle plus fats prehypertension yahoo 75 mg plavix, or fats alone ends in insulin resistance blood pressure chart age 13 purchase plavix 75 mg with amex, downregulation of glucose transport [4446], and; · overexpression in cells results in hyperinsulinemia [47]. These phenotypes mimicked and subsequently validated those that had been seen within the infusion fashions and with glucosamine therapy of explanted tissues [4850]. Discovered by Hart in 1984, this form of glycosylation is dynamic, is commonly discovered on proteins involved in sign transduction, and is aware of changes in glucose flux [53,54]. O-glycosylation is usually reciprocal with phosphorylation and in some circumstances occurs on the identical residues that are otherwise phosphorylated. Initial activation of the pathway is thought to occur through glucose mass action, which is at low insulin concentrations after an overnight fast, and is increased under hyperglycemic conditions. Glucosamine can bypass the rate-limiting step of the pathway and may therefore be used as a tool to examine consequences of activation of the hexosamine pathway. Glucose toxicity 419 happens to happen on the level of normoglycemia in mammals, 5 mM glucose [59]. Exposure of cultured adipocytes to high glucose or glucosamine, or streptozotocin-induced diabetes in mice renders the enzyme insulin resistant and less sensitive to its principal optimistic allosteric regulator, glucose-6-phosphate [69], and this is associated to not adjustments in phosphorylation but somewhat to ranges of O-glycosylation. Thus, even because the insulin signal transduction pathway is being activated, steps are also being taken by the cell to attenuate that acute signal through increased O-glycosylation of most of the same proteins. Human studies, nonetheless, have revealed modest [76] or no [77] results of glucosamine infusion on insulin resistance. The glucosamine infusions may not have reached threshold concentrations for enough lengths of time or could not have focused key tissues similar to liver or adipose tissue. With age and chronic overstimulation of the pathway, nevertheless, animals with chronically increased hexosamine flux exhibit several of the maladaptive options of the sort 2 diabetes syndrome together with weight problems, hyperlipidemia, insulin resistance, and -cell failure 420 Chapter 27 [44,forty seven,80]. Oxidative stress from excess glucose metabolism Another major fate of glucose that has been linked to glucose toxicity is the oxidative stress that results from oxidation of abnormally heavy glucose hundreds. As was the case for the term "glucose toxicity," using the words "oxidative stress" might connote a purely deleterious impact such as the buildup of oxidized and dysfunctional lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids due to excess free radicals and different oxidants. It can also be clear, nevertheless, that the cellular redox state is equally important to the physiologic regulation of metabolism through multiple mechanisms including altering the ratios of decreased to oxidized glutathione, redox status of thiols in proteins such as thioredoxin, activity of key phosphatases, different redox-dependent posttranslational modifications such as protein nitrosylation, levels and activities of adipokines, and others. Although the most obvious supply for these reactive species is oxidative phosphorylation, different sources which might be notably related to diabetes and glucose toxicity include reactive products of superior glycation end-products and glyceraldehyde autoxidation (reviewed in [90]). Oxidative stress and -cell failure in diabetes Increasing evidence hyperlinks oxidative stress provoked by hyperglycemia to -cell harm [91,92]. Interestingly, the latter reference hyperlinks hexosamine signaling to induction of oxidative stress, offering one potential hyperlink between these important processes in glucose toxicity. In addition, cells are programmed to goal most of their glucose to oxidative phosphorylation for signaling of insulin secretion, in order that in states of hyperglycemia there will be an added stress of elevated manufacturing of oxidant species on high of the decreased capacity to reduce those species. Additivity of oxidant stress with excessive concentrations of glucose has been directly demonstrated [94]. These findings have led to multiple studies that reveal that transgenic overexpression of antioxidant enzymes (both cytosolic and mitochondrial superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase) all defend from -cell failure in isolated islets, cultured insulin-producing cells, and rodent fashions [95,96]. As would be predicted from these data, insulin secretory defects and the changes in genes controlling insulin secretion in a number of experimental models of glucose toxicity have also been prevented by numerous antioxidant therapies corresponding to N-acetylcysteine, troglitazone, and aminoguanidine [91,97]. Cellular mechanisms for results of hyperglycemia on insulin secretion Exposure of the cell to experimental continual hyperglycemia induces particular desensitization to glucose whereas the insulin response to other secretagogues similar to arginine [37], leucinenobreak [98], and isoproterenol [99] are either preserved or exaggerated. Such selective desensitization to glucose however not other secretagogues similar to arginine can be seen through the early sorts 1 and a pair of diabetes. This desensitization is considered completely reversible by restoration of normal glucose concentrations [100]. Consistent with these observations, one mechanism by which antioxidants restore normal insulin secretion is direct preservation of mitochondrial function and stimulus-secretion coupling [101]. Oxidative stress and insulin resistance the affiliation of oxidant stress with insulin resistance has been documented in humans for nearly twenty years [102]. These results are mirrored in cell culture models, whereby it has additionally been proven that antioxidants corresponding to -lipoic acid protects towards the consequences of oxidant stress on insulin signaling pathways in cultured adipocytes and myocytes [103]. These studies have prompted trials of antioxidants in humans, whereby short-term improvements in insulin sensitivity are seen [104], although the long-term advantages of antioxidant therapies in sort 2 diabetes have been less encouraging. Part of the rationale for the latter is in all probability going because of the complexity of oxidant stress on insulin signaling and the perform of insulin-responsive tissues. Hence, supply of the right species of antioxidant to the right tissues at sufficiently sustained levels might be a daunting task. Therefore and in contrast to the outcomes obtained in sufferers with type 2 diabetes (see later), insulin sensitivity can be markedly improved and even normalized in kind 1 sufferers by optimizing insulin remedy [20]. The enhanced insulin sensitivity explains why glycemic management may be improved without necessarily having to enhance the every day dose [115,116]. Thus, though the loss of insulin secretion is irreversible in sort 1 diabetes, insulin sensitivity is amenable to marked modification by alterations in glycemic control. Type 2 diabetes Data from each a quantity of cross-sectional and potential research have documented that hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance each precede and predict the following growth of sort 2 diabetes. The etiology of insulin resistance is multifactorial and includes familiar/genetic and acquired parts. In maintaining with this, insulin resistance has been a uniform discovering in patients with kind 2 diabetes and has solely been partially reversed by, for instance, aggressive insulin therapy [7,24,117119]. Both weight loss [23,120123], sulfonylureas [123], and insulin remedy [24,25,123126] enhance insulin secretion. Since neither insulin therapy nor weight reduction have any direct stimulatory results on insulin secretion, their effects could be mediated not directly through diminution of glucose toxicity on -cell secretion. Indeed, the "extrapancreatic impact" (improved insulin sensitivity) of sulfonylureas has been completely attributed to amelioration of insulin resistance via lowering of the plasma glucose concentration [127]. In phrases of practical clinical care, the fact that the core defects that contribute to hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, including extra hepatic glucose production, impaired insulin secretion, and insulin resistance, all improve with management of glycemia implies that management of sort 2 diabetes must be simpler to preserve after a relatively short period of near-normoglycemia. In the biggest of such research 382 Chinese patients have been randomly assigned to therapy with insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents [128]. Treatment was stopped after normoglycemia was maintained for two weeks after an preliminary therapy period of 10 days. Better glycemic management was achieved with insulin remedy than with oral agents and the remission rates had been larger at 1 year in those handled initially with insulin as compared to oral hypoglycemic agents. The acute insulin response was considerably improved by intensive glucose management with insulin. This enhance was sustained at 1 year in the insulin teams however significantly declined in patients treated with oral hypoglycemic brokers [128]. This research in addition to many smaller research (reviewed in [129]) counsel that short-term intensive insulin remedy early in the course of might provide favorable long-term effects on -cell perform. Clinical significance of glucose toxicity Type 1 diabetes After analysis of type 1 diabetes, initiation of insulin remedy induces partial clinical remission in 30% of the patients in the course of the first year [96].
Purchase 75mg plavix free shippingHowever blood pressure high in the morning purchase 75 mg plavix free shipping, despite the ability of the islet cell population to expand in response to some physiologic stimuli blood pressure elderly buy plavix 75 mg with visa, the limited capacity for -cell enlargement arteria yugular buy 75 mg plavix with mastercard, particularly with age pulse pressure 47 cheap plavix 75mg online, becomes a significant drawback in illness states the place cells are targeted for destruction. However, the pancreas is more broadly affected, with overall pancreas dimension being decreased in people with this type of diabetes [68,69], and lack of exocrine tissue occurring near areas of immune infiltration [70]. However, the diploma of infiltration can range widely even among islets from the same animal in various phases of diabetes improvement [73,74].
[newline]Further, the extent of leukocyte infiltration in humans appears to be lower than that seen in animal models, whereas the variability in affected islets is analogous [70,seventy two,75]. That insulitis occurs predominantly around the time of disease onset is consistent with the medical statement that the largest decline in C-peptide responses occurs between 6 months prior to and 12 months following illness diagnosis [77,78]. Despite the variability in detectable insulitis, autoimmune destruction appears to result in eventual elimination of nearly all of cells [70,79]. However, cells can persist for many years into the course of the illness [79,80] and low ranges of -cell replication have been documented in some [81], but not all research [82]. This raises the likelihood that -cell destruction may not be full and that regeneration could also be possible. Specifically, meal-stimulated glucagon responses are exaggerated [85], while glucagon launch in response to hypoglycemia is markedly impaired [86]. These abnormalities may be because of the dearth of oscillating insulin levels, which would usually act to regulate glucagon release [87]. Interestingly, however, once insulitis is resolved, peri-islet extracellular matrix is regenerated, even in the absence of insulin-positive cells, offering further assist for a role of leukocytic infiltration in 74 Chapter 5 the degradation of this extracellular matrix. Fibrosis in the exocrine pancreas has been described [95], suggesting some abnormality in the exocrine pancreas, however this has not been extensively studied. More than a century ago, Opie described decreased cell quantity and accumulation of what was later recognized as islet amyloid [96]. Overall, the extent of -cell loss reported varies widely among studies (063% reduction), more than likely due to the variability of -cell quantity among topics [16,17] and likewise to the positioning of sampling [16]. In animal models, islet glucagon and pancreatic polypeptide immunoreactivity have been reported to be related or increased relative to nondiabetic animals [99,100], while somatostatin immunoreactivity is more variable, being reportedly elevated, similar or decreased compared to nondiabetic animals [99101]. Alterations in density and/or morphology of islet capillaries have been described in a wide selection of rodent fashions of diabetes. Early in the midst of hyperglycemia, distorted islet capillary morphology is current and with extra advanced diabetes, lack of capillary density happens and is incessantly related to islet fibrosis [102108]. Influence of exocrine pancreas abnormalities on islet morphology and performance Diseases affecting the exocrine pancreas are associated with diabetes. Acute pancreatitis has been related to glucose intolerance and impaired insulin release, but this disturbance appears to be momentary [113], suggesting that exocrine pancreas abnormalities can influence islet function. In instances of continual pancreatitis whose primary disease etiology is exocrine in nature, diabetes is current within the majority of instances [114]. However, with improved remedy including lung transplantation, survival has significantly improved in recent times; as a result, different complications of cystic fibrosis at the second are extra common. Pancreatic involvement, particularly important exocrine pancreas fibrosis is the second most typical characteristic of cystic fibrosis, after lung pathology. Accordingly, cystic fibrosis-related diabetes complicates a large proportion of cystic fibrosis instances [117]. This is accompanied by decreased islet -cell volume, which has been documented in a number of research [121,122]. This process has been broadly studied, and numerous mechanisms have been implicated. The literature clearly reveals that chronic exposure of cells to elevated glucose ends in impaired -cell operate [124126], however the knowledge concerning mobile toxicity in response to this nutrient are extra combined. Exposure of cultured -cell strains or islets to excessive glucose can, in some cases, end in elevated -cell demise [127132]. Further in vitro and in vivo research exposing cell to elevated glucose have shown helpful effects with glucose-promoting survival alerts, suppressing apoptosis [135] or resulting in increased -cell replication [136138]. However, much like the observations with elevated glucose, high fats feeding or lipid infusions in vivo result in increased -cell mass, on account of increased -cell replication [62,138]. Culture of human or transgenic mouse islets beneath conditions that favor amyloid formation, for example high glucose, result in amyloid-induced oxidative stress and elevated -cell apoptosis, thereby resulting in a discount in -cell area [155160]. Islet infiltration and release of molecules such as proinflammatory cytokines have clearly been implicated in -cell dying on this form of diabetes [169]. Evidence in favor of a job for islet inflammation includes stories of elevated islet manufacturing of interleukin 1 following chronic high glucose tradition of human islets [127]. Islet interleukin 1 production has also been instructed in fashions of islet amyloid formation [112,161,167]. Summary and future instructions the morphology of the pancreas and pancreatic islet is complex, and disturbances in pancreas and islet volume/arrangement that happen in diabetes are multifactorial. Loss of cells is a standard feature of kind 1-, sort 2-, and cystic fibrosis-related diabetes. However, the mechanisms that underlie this pathology differ considerably among the many varied forms of diabetes. Our understanding of how -cell destruction occurs in type 1 and type 2 diabetes has been improved by numerous research, but we still have a lot to study how this occurs. Emerging areas of curiosity include understanding how changes in islet vasculature, innervation, and extracellular matrix contribute to derangements in islet morphology, which can in flip shed new gentle on the causes of -cell loss in diabetes. Pancreatic morphology in normal and diabetic states seventy seven 18 Bosco D, Armanet M, Morel P, et al. Paradoxical suppression of glucose utilization and lack of compensatory enhance in glucose production, roles of insulin resistance, irregular neuroendocrine responses, and islet paracrine interactions. American Pancreatic morphology in regular and diabetic states 79 89 ninety 91 92 ninety three 94 95 ninety six 97 ninety eight 99 a hundred a hundred and one 102 103 104 105 106 Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 2003;285: E1047E1054. American Journal of Physiology - Endocrinology and Metabolism 2007;293:E1656E1662. The first part of this chapter focuses on the construction of the insulin gene, normal regulation of its transcription, and dysregulation under pathologic circumstances. Space limitations stop us from exhaustively citing the work of all investigators who contributed to this subject. The reader is encouraged to refer to the cited review articles for complete reference lists. Insulin gene expression Structure of the insulin gene the insulin gene is particularly expressed in pancreatic cells, though low ranges of expression have been detected within the mind [1], the thymus [2], and in the yolk sac throughout fetal improvement [3]. The first intron is within the 5 -untranslated area, whereas the second intron interrupts the C-peptide coding sequence. Pancreatic -cell-enriched gene transcription is managed by numerous proteins, including both positive-acting isletenriched transcription elements together with Pax6, Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox-1 (Pdx-1), Neurogenic differentiation 1 (NeuroD1/Beta2), and v-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog A (MafA) [5,6], and ubiquitously Introduction the distinctive property of the pancreatic cell is its ability to secrete insulin to allow circulating glucose levels to be maintained inside a slim physiologic range, regardless of extensive fluctuations in energy intake and expenditure. It is ready to sense the glucose concentration in the extracellular milieu, and adapt its insulin secretion fee via a posh interaction between vitamins, hormones, and neuronal alerts. Insulin gene expression is principally managed by a extremely conserved region mendacity roughly 340 bp upstream of the transcription initiation start, termed the enhancer/promoter management area [14,15]. Considerable progress has been made in defining the numerous completely different cis- and trans-acting factors that ensure exact transcriptional regulation, with the focus right here on describing the -cell-enriched transcription factors most pertinent to metabolically regulated expression, particularly Pdx-1, NeuroD1/Beta2, and MafA. Pdx-1 is a homeodomain protein that performs a major role in pancreatic -cell development and performance [16,17]. Pdx-1 is produced early in rodent pancreatic progenitors, and is crucial to acinar, ductal, and islet endocrine cell formation [5].
75mg plavix otcOccasionally hypertension with chronic kidney disease buy cheap plavix 75mg, a extra rounded mass-like area could additionally be noticed in a small blood pressure 40 year old male buy 75mg plavix overnight delivery, poorly functioning spleen in a affected person with sickle cell anemia hypertension portal plavix 75 mg without prescription. The two circumstances that will trigger this finding are extramedullary hematopoiesis and rests of spleen that regenerate or grow in the setting of autosplenectomy blood pressure of 10060 quality 75mg plavix. When sequestration syndrome occurs within the spleen, the spleen is massive and heterogeneous on imaging studies. The degree of splenic enlargement is in all probability not spectacular as a end result of these patients normally have small, poorly functioning, or nonfunctioning spleens. True aneurysms that are causing symptoms or that happen in patients at improve danger for rupture are repaired. In patients with variceal bleeding, depending upon the etiology of the splenic vein occlusion, it may be necessary to treat the bleeding varices and contemplate the choice of splenectomy so as to prevent subsequent bleeding episodes. Key Points True splenic artery aneurysms are normally asymptomatic and found incidentally. They are usually small, located within the distal splenic artery, and will have wall calcification. Acute occlusive splenic vein thrombosis generally enlarges the vein; collaterals are typically absent. Splenic infarcts are most often peripherally situated and triangular in form with the apex of the triangle oriented toward the splenic hilus. Innumerable, repeated episodes of infarction in sickle cell anemia cause the spleen to turn into small and calcified; that is referred to as auto -splenectomy. Levy Definition the spleen is the most commonly injured intra-abdominal organ in blunt trauma. The spectrum of splenic accidents includes hematoma, laceration, fracture, rupture, and accidents to the splenic artery and vein. Infarction, pseudoaneurysm, arteriovenous fistula, and splenosis might occur as a consequence of trauma. Demographic and Clinical Features Traumatic accidents to the spleen may happen in all age teams. Falls, sports injuries, and direct blows to the abdomen and chest are other mechanisms of blunt injuries. The spleen may be injured from penetrating trauma and iatrogenic injuries during surgical and endoscopic procedures. Rib fractures are commonly present in sufferers with splenic accidents and injuries to different organs are reported to happen in as a lot as 40% of cases. Patients may be hemodynamically unstable from energetic hemorrhage and hypovolemic shock or unable to manifest symptoms because of concurrent harm to the top or spine. Some patients could have few or no signs at initial presentation, while others will have left-upper-quadrant ache and tenderness. The spleen has a thin capsule and a delicate, spongy parenchyma that makes it highly vulnerable to harm when compressive and decelerating forces are put upon the upper stomach. Furthermore, its position beneath the ribs makes it vulnerable to laceration when the ribs are fractured. Arterial-phase scanning and elective portal venousphase scanning has been proven to be correct within the detection of organ harm. The higher-attenuation areas inside the hematoma are consistent with acute blood. There is active extravasation of high-attenuation intravenous contrast from the surface of the spleen (arrows in A and B). The amount of extravasated contrast materials elevated from the arterial-phase image (A) to the portal venousphase picture (B), according to active bleeding. There is retraction of the splenic capsule at the web site of injury, consistent with scar. Acute hematomas are hyperattenuating relative to the splenic parenchyma on an unenhanced scan. During intravenous distinction administration, the normal perfused spleen enhances; this aids within the detection of intraparenchymal hematomas, that are hypoattenuating relative to the conventional spleen. Over time, hemorrhage turns into decrease in attenuation and should turn into tough to distinguish from free fluid. They are crescent-shaped and when massive and flatten the adjacent splenic parenchyma. Eventually they is probably not discernible or there could additionally be focal atrophy of the spleen at the website of damage. The time period shattered spleen has been utilized to the discovering of severe disruption of the splenic parenchyma. If the splenic artery is injured without important splenic parenchymal injury, a pseudoaneurysm may kind and splenic infarction may also happen. On delayed imaging, active extravasation remains extremely attenuated; it increases in dimension and modifications configuration owing to the buildup of blood and contrast at the website. Delayed rupture is believed to happen from low-grade venous hemorrhage that was not detected on initial imaging. In addition, progression of lacerations could happen and pseudoaneurysms might develop within the days following trauma. Management/Clinical Issues Controversy continues to exist concerning the administration of splenic accidents, and specific administration algorithms differ amongst institutions. However, conservative administration and splenic salvage procedures, if attainable, are most popular. Key Points Splenic hematomas could additionally be intraparenchymal, subcapsular, or perisplenic. Active extravasation is linear, irregular highattenuation extravasated intravenous contrast that is still excessive attenuation; it increases in size and modifications configuration on delayed scans. Accurate localization and definition of splenic and splenic vascular accidents is essential for figuring out applicable management. Appearance of stable organ damage with contrast-enhanced sonography in blunt abdominal trauma: preliminary expertise. Levy Definition the peritoneum is a serosal membrane that lines the surface of the intraperitoneal portion of the abdominal cavity. It covers the intraperitoneal organs and varieties the mesenteries and peritoneal ligaments. The function of the peritoneum is to provide a smooth surface that helps the intraperitoneal viscera to transfer. The muscular tissues and fascia of the anterior stomach wall present help and protection for the contents of the belly cavity. Normal Anatomy Peritoneal Cavity the stomach and pelvis are compartmentalized into discrete anatomic spaces: the peritoneal cavity, retroperitoneum, and extraperitoneal pelvis. The peritoneum defines the boundaries of these three main compartments as a result of it strains the peritoneal cavity, separating it from the retroperitoneum and the extraperitoneal pelvis. The visceral peritoneum partially or utterly covers the intraperitoneal organs (stomach, jejunum, ileum, transverse colon, sigmoid colon, liver, and spleen), mesenteries, and peritoneal ligaments.
Discount 75mg plavix fast deliveryIn fact arrhythmia emedicine discount plavix 75 mg online, insulin secretion should cope with acute (meals high blood pressure medication toprol xl plavix 75mg line, exercise hypertension diabetes 75mg plavix free shipping, tense events) and long-term (body weight achieve or loss blood pressure chart during pregnancy buy cheap plavix 75mg online, aging, pregnancy) modifications. Whereas the amount of insulin released daily has been reported to range 2070 U (mainly relying on body weight) [26,27], capturing the multifaceted features of insulin secretion in vivo is a tough task [2830]. However, the recent use of human islets isolated from the pancreas of organ donors has allowed the direct research of -cell insulin release under totally different conditions, showing that several of the insulin secretion properties observed in vivo (dynamics, oscillatory sample, metabolic and/or pharmacologic perturbations) may be reproduced ex vivo [18,3137]. Introduction Insulin-producing -cells are the predominant endocrine cell sort in pancreatic islets, comprising 5080% of islet cells [13]. Studies with autoptic samples, organ donor specimens, and surgical circumstances have found that -cell mass in the human pancreas might range from 0. Islet insulin content material has been reported to be 100500 U per islet [1620], however some islets might contain more than one thousand U insulin [20]. Insulin should be equipped to physique tissues in amounts, time-dynamics and adaptability able to preserve plasma glucose -Cell mass in sort 2 diabetes Although quantification of -cells within the human pancreas is a difficult task, morphometric analyses have been performed by a quantity of authors to assess -cell mass (when the load of pancreas specimens was available), volume (usually assuming that the islets are spherical), and/or area (insulinpositive proportions within the islets or the pancreatic tissue) [47,9,10,1215,3846]. Early work reported that whole islet quantity was 3050% lower in histology samples from type 2 diabetic topics as in comparison with nondiabetic individuals [38,39]. A reduction of complete islet quantity in diabetic verus nondiabetic pancreata was additionally shown [40,41], which grew to become International Textbook of Diabetes Mellitus, Fourth Edition. Clark and colleagues reported a 24% reduction in -cell space in their sequence of sort 2 diabetic pancreas samples [45], and islet -cell volume and total -cell mass have been discovered to be significantly decrease (30%) in specimens from Japanese sort 2 diabetic sufferers than in samples from nondiabetic people [4]. In the nonobese group, diabetes was associated with 41% discount of -cell quantity. Increased -cell apoptosis in diabetic islets has been confirmed by electron microscopy [47]. These changes are accompanied by increased numbers of cells optimistic for activated caspase-3 [48] as well as higher exercise of caspase-3 and caspase-8 [18], that are key molecules in the induction and execution of apoptosis. However, types of programmed cell death apart from apoptosis have been described [49]. One includes autophagy, which is a type of cell dying that occurs without marked chromatin condensation and is accompanied by large vacuolization of the cytoplasm [5557]. In general, usually functioning autophagy has a beneficial role for cells (including the -cell [5860]) because it regulates the turnover of aged proteins and eliminates broken constructions and organelles [60]. However, cells that bear altered autophagy may die in a nonapoptotic method [5557]. It may be therefore concluded that -cell death is increased in sort 2 diabetic patients due to enhanced apoptosis and other types of cell demise, which may contribute to -cell failure on this illness. Normally, insulin-positive cells appear within the human pancreas at around the eighth week of gestation; at 10 weeks postconception all clusters containing greater than 10 insulin-positive cells have developed a close relationship with vascular constructions [68]. After an additional 23 weeks, human fetal islets contain cells independently immunoreactive for insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide [68]. After start, as shown by the study of autoptic pancreatic samples from subjects aged 2 to 20 years, -cell mass expands several-fold from infancy to adulthood, mainly due to growth in islet dimension rather than quantity, a course of pushed by the speed of -cell replication [21]. After the age of 2030 years, nevertheless, the rate of islet -cell replication appears negligible, as proven in two unbiased research analyzing lipofuscin accumulation and thymidine incorporation in human -cells [71,72]. This implies that -cell regeneration in adults may happen at a very low price, if at all. Nevertheless, -cell mass in adult human people can enhance, corresponding to happens in obesity and through being pregnant [57,9,seventy three,74]. However, the same authors, in a more focused article, while confirming the augmented -cell mass in autoptic pancreatic samples of obese subjects, have been unable to find variations by way of apoptosis or regeneration, as assessed by some of the at present available surrogate markers (Ki67, insulin-positive cells in the duct wall) [73]. In this case, the authors discovered that each -cell replication and neogenesis had been considerably enhanced in the obese samples in the face of comparable charges of apoptosis. Although, for apparent causes, knowledge in people are very scanty, one examine has reported on the morphometry of the pancreatic islets throughout gestation in people [74]. The authors collected pancreases obtained at autopsy from ladies who had died while pregnant, and located that the pancreatic fractional -cell area was elevated by roughly 1. Mean -cell dimension was not completely different, and in pregnancy there have been more small islets quite than a rise in islet dimension or -cells per islet. No enhance in -cell replication or change in -cell apoptosis was detected, however duct cells positive for insulin and scattered -cells had been increased with being pregnant, again suggesting, although not directly, a attainable preminent function of -cell neogenesis. Interestingly, in a case of gestational diabetes it has been observed that complete insulin space was reduced, not due to increased apoptosis but decreased regeneration [76]. The problem of -cell regeneration has been investigated in a couple of morphometric research with pancreases from nondiabetic and sort 2 diabetic people (Table 24. It was initially reported that there was no vital distinction within the frequency of -cell replication (as assessed by Ki67 protein staining) between overweight nondiabetic and kind 2 diabetic subjects or lean nondiabetic and sort 2 diabetic subjects [6]. Similarly, when neogenesis was indirectly quantified by counting duct cells immunoreactive for insulin, no distinction was found between the obese or lean nondiabetic and type 2 diabetic cases [6]. Altogether, the out there info, obtained with the use of surrogate markers and indexes of regeneration, indicates Table 24. It is subsequently quantitatively incongruous that a deficit in -cell mass could be the sole reason for the useful impairment. Secondly, in pancreatectomized patients and in topics who bear partial pancreas removal for the purpose of residing organ donation, diabetes tends to develop more incessantly over the years when -cell mass declines by more T2D2 T2D3 T2D4 than 50% [8184]. Finally, it has been clearly proven that any treatment leading to amelioration of glycemic management is related to partial reversal of -cell dysfunction [8890]. As a consequence, -cell secretory dysfunction is the dominant defect within the majority of diabetic patients. Although preliminary work was not able to present variations in insulin secretion between nondiabetic and kind 2 diabetic islets [94,95], research during the last 23 a long time have persistently demonstrated defects of insulin release from kind 2 human diabetes islets [18,36,9698]. In a report printed in 1994, it was proven that the release of insulin evoked by glucose was decrease in sort 2 diabetic than in nondiabetic islets [96]. However, the secretory response to a mix of L-leucine and L-glutamine appeared less severely altered [96]. In a more recent study, islets isolated from eight diabetic and 9 nondiabetic donors have been evaluated by in vitro islet perifusion experiments [98]. Insulin secretion during glibenclamide and arginine stimulation was additionally decrease from diabetic islets than from control islets; of observe, in this series kind 2 diabetic islets released more insulin in response to non-glucose stimuli than in response to glucose. Interestingly, comparable adjustments in insulin secretion can be induced in nondiabetic human islets by prolonged exposure to elevated levels of free fatty acids (in particular, palmitate) or glucose [31,99102], mimicking findings reported in in vivo studies [103,104]. All these data clearly point out that type 2 diabetic -cells have faulty insulin secretory behavior, which contributes to the event of hyperglycemia at least in part independently of -cell mass. Disruption of -cell dialogue within the islet It has long been acknowledged that -cells dialogue with one another and with the opposite islet endocrine cells, primarily by way of autocrine and paracrine communication [105111]. This is made possible by the peculiar group of endocrine cells in human islets [3,112]-allowing more than 70% of -cells to be in contact with non-cells [112]-and the abundance of gap junctions (containing connexin proteins) and other cellcell adhesion complexes [109,113115].
Buy plavix 75mg fast deliveryFatty acyl CoAs high blood pressure quiz plavix 75 mg mastercard, that are recognized to inhibit insulin signaling [341 hypertension journals ranking generic 75mg plavix otc,342] wireless blood pressure monitor generic 75 mg plavix with amex, are also considerably elevated in muscle in diabetic topics [338 arteriosclerosis discount plavix 75mg with amex,343]. However, there is also proof that the mitochondrial defect is acquired, at least partly [349351]. Treatment of diabetic patients with pioglitazone markedly improves insulin sensitivity in association with a discount in intramyocellular lipid and fatty acyl CoA concentrations. The decrement in muscle fatty acyl CoA content material is closely related to the development in insulin-stimulated muscle glucose disposal [340,343]. Reduced intramyocellular fatty acyl CoA content with acipimox, a potent inhibitor of lipolysis, brought on an analogous enchancment in insulin-mediated glucose disposal [338,339]. Increased intramyocellular ranges of diacylglycerol [330,352] and ceramides [353,354] have been demonstrated in sort 2 diabetic and overweight nondiabetic subjects and shown to be associated to the insulin resistance and impaired insulin signaling in muscle. Alpha cell and glucagon It long has been known that the basal plasma glucagon concentration is elevated in sort 2 diabetic people [184186, 357,358]. There also is proof that the liver is hypersensitive to the stimulatory impact of glucagon in hepatic gluconeogenesis [185]. The kidney: elevated glucose reabsorption the kidney filters 162 g ([glomerular filtration fee = one hundred eighty L day-1] Ч [fasting plasma glucose = 900 mg L-1]) of glucose every day. Thus, an adaptive response by the kidney to conserve glucose, which is important to meet the vitality demands of the physique, particularly the brain and different neural tissues which have an obligate want for glucose, becomes maladaptive within the diabetic patient. Instead of dumping glucose within the urine to appropriate the hyperglycemia, the kidney chooses to hold on to the glucose. Even worse, the power of the diabetic kidney to reabsorb glucose is augmented by an absolute increase within the renal reabsorptive capacity for glucose. The present epidemic of diabetes is being driven by the epidemic of weight problems [369]. Porte and colleagues [370373] were amongst the first to show that, in rodents, insulin was a robust appetite suppressant. Obese people, both diabetic and nondiabetic, have moderate-to-severe insulin resistance with compensatory hyperinsulinemia. Nonetheless, food consumption is increased in overweight subjects regardless of the presence of hyperinsulinemia which should suppress the appetite. Therefore, one might postulate that the insulin resistance in peripheral tissues also extends to the brain. After glucose ingestion, two hypothalamic areas with consistent inhibition have been famous: the decrease posterior hypothalamus, which incorporates the ventromedial nuclei, and the higher posterior hypothalamus, which contains the paraventricular nuclei. In each of those hypothalamic areas, which are key centers for appetite regulation, the magnitude of the inhibitory response following glucose ingestion was reduced in overweight, insulin-resistant, regular glucose-tolerant topics, and there was a delay within the time taken to reach the maximum inhibitory response, even though the plasma insulin response was markedly increased within the overweight group. Nonetheless, these outcomes recommend that the mind, like other organs (liver, muscle, and fat) within the body, are proof against insulin. Westermark P, Wilander E: the affect of amyloid deposits on the islet quantity in maturity onset diabetes mellitus. Vaxillaire M, Froguel P: Monogenic diabetes within the younger, pharmacogenetics and relevance to multifactorial forms of sort 2 diabetes. Role of alterations in systemic, hepatic, and muscle lactate and alanine metabolism. Evidence for lowered insulin-dependent muscle glucose transport or phosphorylation exercise in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Insulin action and binding in isolated hepatocytes, insulin receptor construction, and kinase activity. A lesson in metabolic regulation inspired by the glucokinase glucose sensor paradigm. Identification of a protein kinase cascade of major significance in insulin sign transduction. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society London Series B: Biological Sciences 1999;354:485495. Kelley D, Mokan M, Mandarino L: Intracellular defects in glucose metabolism in overweight sufferers with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus 399 338 Bajaj M, Suraamornkul S, Romanelli A, et al. The risk variants are widespread in the population, have only a small impact on disease risk and together solely explain a fraction of the heritability of the illness. The diabetic spectrum Diabetes is a gaggle of metabolic ailments characterised by hyperglycemia ensuing from defects in insulin secretion, insulin motion, or both. The continual hyperglycemia of diabetes is associated with long-term harm, dysfunction, and failure of various organs, particularly the eyes, kidneys, nerves, coronary heart, and blood vessels. These disease sorts could probably be divided further into subtypes presumably representing completely different illness mechanisms. The diabetes epidemic Worldwide prevalence figures estimate that there have been 371 million diabetic patients in 2012 and more than 500 million are anticipated in 2030. In a situation of affluence most people are probably to overconsume International Textbook of Diabetes Mellitus, Fourth Edition. One attainable cause for this is that genetic selection has favored energy-preserving genotypes (so called thrifty genotypes); people residing in an surroundings with unstable food provide might maximize their chance of survival by effectively storing power in occasions of surplus [2]. Twin-studies have estimated the genetic part by comparing illness concordance in dizygotic twins with concordance in monozygotic twins. In these research probandwise concordance rates (number of affected twins having a diabetic co-twin) for monozygotic twins vary between 34 and one hundred pc [36]. However, this statistic also varies relying on the cohort and population studied. There are also large differences between ethnic teams that appear to depend upon genetic factors. While a part of the noticed ethnic variability could be attributed to environmental and cultural elements some of the variation appears to depend upon genetic variations. Concordant twins usually tend to take part in a examine and the proportion of people with undiagnosed diabetes might differ compared to the overall inhabitants. There are many possible explanations for this including a job for the intrauterine environment in programming events later in life. Originally, disease-causing loci have been recognized primarily by linkage evaluation, using the lengthy stretches of linkage in affected households. For loci recognized by whole-genome affiliation only loci reaching genome-wide significance (p < 5 Ч 10-8) are included. Linkage analysis has, nonetheless, been much less helpful for identifying genes causing advanced illnesses.
References - Stanek E, Aubert R, Flockhart D, et al: A national study of the effect of individual proton pump inhibitors on cardiovascular outcomes in patients treated with clopidogrel following coronary stenting: The clopidogrel Medco outcomes study. Presented at Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Las Vegas, NV May 6, 2009.
- Levy HL, Guldberg P, Guttler F, et al. Congenital heart disease in maternal phenylketonuria: report from the Maternal PKU Collaborative Study. Pediatr Res. 2001;49:636-42.
- Prieto D, Simonsen U, Martin J, et al: Histochemical and functional evidence for a cholinergic innervation of the equine ureter, J Auton Nerv Syst 47:159, 1994.
- Enke BU, Bokenkamp A, Offner G, et al. Response to diphtheria and tetanus booster vaccination in pediatric renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 1997;64:237-241.
- Roberts MJ, Thiele A. Attention and contrast differently affect contextual integration in an orientation discrimination task. Exp Brain Res 2008;187:535-49.
- Gay WA Jr, Ebert PA: Functional, metabolic, and morphologic effects of potassium-induced cardioplegia, Surgery 74:284-290, 1973.
- Sear JW: Kidney dysfunction in the postoperative period, Br J Anaesth 95:20-32, 2005.
|