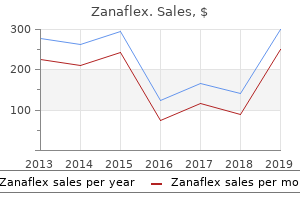
Zanaflex
Marilyn L. Yucaitis, RNBA, CEN, TNCCP, - ENPC
- Department of Emergency Medicine
- Mount Sinai Hospital
- Chicago, IL
Discount 2 mg zanaflex mastercardFibrin monomers hyperlink spontaneously by hydrogen bonds to kind a unfastened insoluble fibrin polymer muscle relaxant robaxin generic zanaflex 4 mg fast delivery. After cleavage by thrombin of small fibrinopeptides A and B from the and chains spasms meaning in telugu cheap 4 mg zanaflex amex, fibrin monomer consists of three paired spasms near temple order 4 mg zanaflex with mastercard, and chains which rapidly polymerise muscle relaxant eperisone hydrochloride buy 4mg zanaflex fast delivery. This cell provides the basement membrane that normally separates collagen, elastin and fibronectin of the subendothelial connective tissue from the circulating blood. Loss of or injury to the endothelium results in each haemorrhage and activation of the haemostatic mechanism. The decreased blood flow allows contact activation of platelets and coagulation factors. Endothelial cells produce substances that may provoke coagulation, cause vasodilatation, inhibit platelet aggregation or haemostasis, or activate fibrinolysis. This continuing platelet aggregation promotes the expansion of the haemostatic plug, which soon covers the uncovered connective tissue. The unstable main haemostatic plug produced by these platelet reactions within the first minute or so following injury is normally adequate to provide momentary management of bleeding. Stabilization of the platelet plug by fibrin Definitive haemostasis is achieved when fibrin, formed by blood coagulation, is added to the platelet mass and by plateletinduced clot retraction/compaction. Platelet aggregation and launch reactions speed up the coagulation course of by offering ample membrane phospholipid. The fibrin element of the haemostatic plug increases because the fused platelets utterly degranulate and autolyse, and after a number of hours the entire haemostatic plug is transformed into a strong mass of cross linked fibrin. Chapter 24: Platelets, blood coagulation and haemostasis / 275 Coagulation factor inhibitors It is necessary that the impact of thrombin is limited to the positioning of injury. There can additionally be direct inactivation of thrombin and other serine protease factors by different circulating inhibitors, of which antithrombin is the most potent. The action of protein C is enhanced by another vitamin Kdependent protein, S, which binds protein C to the platelet floor. An endothelial protein C receptor localizes protein C to the endothelial floor, promoting protein C activation by the thrombin�thrombomodulin advanced. As with different serine proteases, activated protein C is subject to inactivation by serum protease inactivators (serpins). Blood move At the periphery of a broken area of tissue, blood flow quickly achieves dilution and dispersal of activated components before fibrin formation has occurred. Activated components are destroyed by liver parenchymal cells and particulate matter is removed by liver Kupffer cells and other reticuloendothelial cells. Fibrinolysis Fibrinolysis (like coagulation) is a standard haemostatic response to vascular damage. Plasminogen, a proenzyme in blood and tissue fluid, is transformed to the serine protease plasmin by activators either from the vessel wall (intrinsic activation) or from the tissues (extrinsic activation). Plasmin technology on the web site of injury limits the extent of the evolving thrombus. The break up merchandise of fibrinolysis are also aggressive inhibitors of thrombin and fibrin polymerization. Protein S is a cofactor that facilitates binding of activated protein C to the platelet surface. Cleavage of peptide bonds in fibrin and fibrinogen produces a variety of break up (degradation) products. Large quantities of the smallest fragments can be detected within the plasma of patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (see p. Circulating plasmin is inactivated by the potent inhibitors 2antiplasmin and 2macroglobulin. A variety of simple tests are employed to assess the platelet, vessel wall and coagulation elements of haemostasis. Blood rely and blood film examination As thrombocytopenia is a standard explanation for irregular bleeding, sufferers with suspected bleeding disorders ought to initially have a blood rely including platelet count and blood film examination. In addition to establishing the presence of thrombocytopenia, the cause could additionally be apparent. Platelet depend and the tests of platelet operate are also used in screening patients with a bleeding dysfunction (p. Tissue thromboplastin (a mind extract) or [synthetic] tissue issue with lipids and calcium is added to citrated plasma. Diluted bovine thrombin is added to citrated plasma at a focus giving a clotting time of 14�16 s with regular subjects. This normally requires a provide of plasma from patients with hereditary deficiency of the consider query or artificially produced factordeficient plasma. The corrective impact of the unknown plasma on the prolonged clotting time of the deficient substrate plasma is then in contrast with the corrective impact of regular plasma. The test concerned the appliance of pressure to the higher arm with a blood stress cuff, after which small incisions are made within the flexor surface forearm skin. The bleeding time is prolonged in thrombocytopenia but is regular in vascular causes of abnormal bleeding. Tests of platelet function Conventional platelet aggregometry measures the fall in mild absorbance in plateletrich plasma as platelets aggregate. Initial (primary) aggregation is caused by an external agent; the secondary response is attributable to aggregating brokers launched from the platelets themselves. Flow cytometry is now increasingly utilized in routine apply to establish platelet glycoprotein defects. The analysis might give falsenegative results with relatively frequent platelet defects. Ddimer is a measurement of fibrin degradation merchandise and is a sign of sequential thrombin after which plasmin activity. The take a look at could be carried out on citrated plasma samples together with simple coagulation checks. There are many causes of a excessive Ddimer, together with infection, most cancers and pregnancy, in addition to venous thromboembolism. Blood coagulation in vivo in response to vascular Normal haemostasis requires vasoconstriction, platelet aggregation and blood coagulation. The intact endothelial cell separates collagen and other subendothelial connective tissues that would stimulate platelet aggregation from circulating blood. The endothelial cells additionally produce prostacyclin, nitric oxide and an ectonucleotidase, which inhibit platelet aggregation. Platelets are produced from megakaryocytes in the bone marrow stimulated by thrombopoietin. They have floor glycoproteins which facilitate direct adherence to subendothelial tissues and likewise, by way of von Willebrand factor, to collagen, to other platelets (aggregation) and to fibrinogen.
Syndromes - Children: 42 to 135
- Drinking a large amount of alcohol
- Long-term loss of brain function (dementia)
- Celiac sprue
- Nosebleeds (epistaxis)
- Paralysis
- Other problems within the rectum
- Place a cold pack or cold wet wash cloth on the outer ear for 20 minutes to reduce pain.
- Headache
Generic zanaflex 2mgIt anastomoses with the anterior circum ex humeral artery muscle relaxant benzo zanaflex 4 mg, and with branches from the profunda brachii muscle relaxers to treat addiction cheap zanaflex 2mg without a prescription, suprascapular spasms in head buy zanaflex 2mg cheap, and thoracoacromial arteries spasms stomach area purchase zanaflex 2 mg without prescription. Clinical app Central venous entry through the subclavian/axillary vein There are a variety of routes by way of which central venous access may be obtained. The subclavian route is a misnomer that is still the popular term in clinical follow. Axillary vein the axillary vein begins at the lower margin of the teres major muscle and is the continuation of the basilic vein. The axillary vein passes via the axilla medial and anterior to the axillary artery and becomes the subclavian vein because the vessel crosses the lateral border of rib I at the axillary inlet. Tributaries of the axillary vein typically observe the branches of the axillary artery. Other tributaries embrace brachial veins that observe the brachial artery, and the cephalic vein. The cephalic vein is an excellent cial vein that drains the lateral and posterior components of the hand, the forearm, and the arm. In the area of the shoulder, it passes into an inverted triangular cleft (the clavipectoral triangle) between the deltoid muscle, pectoralis main muscle, and the clavicle. In the superior part of the clavipectoral triangle, the cephalic vein passes deep to the clavicular head of the pectoralis major muscle and pierces the clavipectoral fascia to be part of the axillary vein. Brachial plexus the brachial plexus is a somatic plexus shaped by the anterior rami of C5 to C8, and most of the anterior ramus of T1. It originates within the neck, passes laterally and inferiorly over rib I, and enters the axilla. The elements of the brachial plexus, from medial to lateral, are roots, trunks, divisions, and cords. All main nerves that innervate the higher limb originate from the brachial plexus, principally from the cords. Proximal elements of the brachial plexus are posterior to the subclavian artery within the neck, whereas extra distal areas of the plexus encompass the axillary artery. Roots 362 the roots of the brachial plexus are the anterior rami of C5 to C8, and most of T1. Close to their origin, the roots obtain gray rami communicantes from the sympathetic Regional anatomy � Axilla trunk. These carry postganglionic sympathetic bers onto the roots for distribution to the periphery. The roots and trunks enter the posterior triangle of the neck by passing between the anterior scalene and middle scalene muscles and lie superior and posterior to the subclavian artery. The posterior cord happens posterior to the second a part of the axillary artery and originates because the union of all three posterior divisions; it accommodates contributions from all roots of the brachial plexus (C5 to T1). The inferior trunk lies on rib I posterior to the subclavian artery; the center and superior trunks are extra superior in position. Most of the main peripheral nerves of the higher limb originate from the cords of the brachial plexus. Generally, nerves related to the anterior compartments of the higher limb come up from the medial and lateral cords and nerves associated with the posterior compartments originate from the posterior cord. The three posterior divisions mix to type elements of the brachial plexus that give rise to nerves related to the posterior compartments. In addition to small segmental branches from C5 to C8 to muscles of the neck and a contribution of C5 to the phrenic nerve, the roots of the brachial plexus give rise to the dorsal scapular and lengthy thoracic nerves. The dorsal scapular nerve: originates from the C5 root of the brachial plexus, passes posteriorly, usually piercing the middle scalene muscle within the neck, to attain and travel alongside the medial border of the scapula, and innervates the rhomboid main and minor muscles from their deep surfaces. Cords the three cords of the brachial plexus originate from the divisions and are related to the second a part of the axillary artery. Clinical app Damage to lengthy thoracic nerve A mastectomy (surgical removing of the breast) includes excision of the breast tissue to the pectoralis main muscle and fascia. Within the axilla, the breast tissue have to be removed from the medial axillary wall. Damage to this nerve can lead to paralysis of the serratus anterior muscle producing a attribute "winged" scapula. This nerve also could be injured during placement of chest tubes or by trauma to the lateral physique wall. The suprascapular nerve (C5 and C6): originates from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus. The nerve to subclavius muscle (C5 and C6) is a small nerve that: originates from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus, passes anteroinferiorly over the subclavian artery and vein, and innervates the subclavius muscle. Branches of the lateral cord Three nerves originate completely or partly from the lateral twine. Regional anatomy � Axilla the lateral pectoral nerve is the most proximal of the branches from the lateral wire. It passes anteriorly, along with the thoracoacromial artery, to penetrate the clavipectoral fascia that spans the gap between the subclavius and pectoralis minor muscles, and innervates the pectoralis main muscle. It passes laterally to penetrate the coracobrachialis muscle and passes between the biceps brachii and brachialis muscular tissues in the arm, and innervates all three exor muscular tissues in the anterior compartment of the arm, terminating as the lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm. The lateral root of median nerve is the biggest terminal branch of the lateral cord and passes medially to be a part of an identical branch from the medial twine to type the median nerve. Some of these branches pass by way of the muscle to attain and supply the pectoralis major muscle. Other branches sometimes cross across the inferior or lateral margin of the pectoralis minor muscle to reach the pectoralis major muscle. The medial cutaneous nerve of arm (medial brachial cutaneous nerve) passes via the axilla and into the arm where it penetrates deep fascia and provides pores and skin over the medial facet of the distal third of the arm. Fibers of the medial cutaneous nerve of arm innervate the upper a half of the medial surface of the arm and oor of the axilla. The medial cutaneous nerve of forearm (medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve) originates simply distal to the origin of the medial cutaneous nerve of arm. It passes out of the axilla and into the arm where it offers off a branch to the pores and skin over the biceps brachii muscle, after which continues down the arm to penetrate the deep fascia with the basilic vein, persevering with inferiorly to provide the skin over the anterior surface of the forearm. It receives a communicating department from the lateral pectoral nerve after which passes anteriorly between the axillary artery and axillary vein. However, near its origin, it often receives a speaking branch from the lateral root of the median nerve originating from the lateral cord and carrying bers from C7. The ulnar nerve passes by way of the arm and forearm into the hand, the place it innervates all intrinsic muscles of the hand (except for the three thenar muscular tissues and the two lateral lumbrical muscles). On passing via the forearm, branches of the ulnar nerve innervate the exor carpi ulnaris muscle and the medial half of the exor digitorum profundus muscle. The ulnar nerve innervates skin over the palmar floor of the little nger, medial half of the ring nger, and related palm and wrist, and the skin over the dorsal floor of the medial a half of the hand. The median nerve is formed anterior to the third a part of the axillary artery by the union of lateral and medial roots originating from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus. It passes into the arm anterior to the brachial artery, through the arm into the forearm the place branches innervate most of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm (except for the exor carpi ulnaris muscle and the medial half of the exor digitorum profundus muscle, that are innervated by the ulnar nerve).
Zanaflex 4mg fast deliveryThe cycle is divided into the mitotic section (M phase) muscle relaxer kidney pain order zanaflex 4mg online, throughout which the cell bodily divides muscle relaxant gabapentin purchase zanaflex 2mg without a prescription, and interphase spasms when excited discount zanaflex 2 mg overnight delivery, during which the chromosomes are duplicated and cell development occurs prior to kidney spasms no pain discount 4mg zanaflex mastercard division. These genes are incessantly mutated in the myeloid malignancies (see Chapters thirteen, 15 and 16). Apoptosis Apoptosis (programmed cell death) is a regulated process of physiological cell demise during which individual cells are triggered to activate intracellular proteins that result in the demise of the cell. It is an important process for sustaining tissue homeostasis in haemopoiesis and lymphocyte growth. An instance of this mechanism is proven by activated cytotoxic T cells expressing Fas ligand which induces apoptosis in goal cells. Following dying, apoptotic cells display molecules that result in their ingestion by macrophages. As properly as molecules that mediate apoptosis there are a number of intracellular proteins that shield cells from apoptosis. Many of the genetic adjustments associated with malignant illness result in a lowered rate of apoptosis and hence extended cell survival. Apoptosis is the traditional destiny for many B cells undergoing selection within the lymphoid germinal centres. Several translocations resulting in the technology of fusion proteins, similar to t(9;22), t(1;14) and t(15;17), additionally end in inhibition of apoptosis (see Chapter 11). Cytochrome c binds to the cytoplasmic protein Apaf1 leading to activation of caspases. Necrosis is demise of cells and adjacent cells due to ischaemia, chemical trauma or hyperthermia. There is often an inflammatory infiltrate in response to spillage of cell contents. It may be involved in cell death but in some situations additionally in sustaining cell survival by recycling vitamins. SummAry Haemopoiesis (blood cell formation) arises from Adhesion molecules are a large household of glycoproteins pluripotent stem cells within the bone marrow. Stem cells give rise to progenitor cells which, after cell divisions and differentiation, type purple cells, granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils), monocytes, platelets and B and T lymphocytes. Haemopoiesis in adults is confined to the central skeleton but in infants and young children haemopoietic tissue extends down the lengthy bones of the legs and arms. Stem cells reside within the bone marrow in niches formed by stromal cells and flow into within the blood. Growth factors attach to specific cell receptors and produce a cascade of phosphorylation events to the cell nucleus. Apoptosis is a physiological means of cell dying resulting from activation of caspases. The most numerous are red cells which are specialized for carriage of oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and of carbon dioxide within the reverse direction (Table 2. They have a four month lifespan, whereas the smallest cells, platelets concerned in haemostasis, flow into for under 10 days. The pink cells and platelets are counted and their diameter and different parameters measured by an automated cell counter. This additionally enumerates the various kinds of white cell by circulate cytometry and detects irregular cells. We every make approximately 1012 new erythrocytes (red cells) each day by the complex and finely regulated process of erythropoiesis. Erythropoiesis passes from the stem cell through the progenitor cells, colonyforming Table 2. The earlier cells are larger, with more basophilic cytoplasm and a more open nuclear chromatin sample. The cytoplasm of the later cells is extra eosinophilic because of haemoglobin formation. This course of happens in an erythroid niche by which about 30 erythroid cells at various levels of improvement surround a central macrophage. The pronormoblast is a big cell with dark blue cytoplasm, a central nucleus with nucleoli and barely clumped chromatin. It offers rise to a collection of progressively smaller normoblasts by numerous cell divisions. A completely pinkstaining mature erythrocyte results which is a nonnucleated biconcave disc. They seem in the blood if erythropoiesis is happening outside the marrow (extramedullary erythropoiesis) and likewise with some marrow illnesses. Normally, 90% of the hormone is produced within the peritubular interstitial cells of the kidney and 10% in the liver and elsewhere. Erythropoietin manufacturing subsequently increases in anaemia, and also when haemoglobin for some metabolic or structural cause is unable to hand over O2 normally, when atmospheric O2 is low or when defective cardiac or pulmonary perform or damage to the renal circulation impacts O2 delivery to the kidney. Erythropoietin stimulates erythropoiesis by rising the number of progenitor cells dedicated to erythropoiesis. In infants, the marrow cavity might expand into cortical bone leading to bone deformities with frontal bossing and protrusion of the maxilla (see p. Conversely, elevated O2 supply to the tissues (because of an increased pink cell mass or because haemoglobin is able to release its O2 more readily than normal) reduces the erythropoietin drive. They are excessive in anaemia except this is due to renal failure and if a tumour secreting erythropoietin is current, however low in extreme renal illness or polycythaemia vera. It is given subcutaneously both 3 times weekly or once every 1�2 weeks or each 4 weeks, depending on the indication and on the preparation used (erythropoietin alpha or beta, darbepoetin alpha (a heavily glycosylated longeracting form), or Micera the longest acting preparation). A low serum erythropoietin level previous to remedy is effective in predicting an effective response. Sideeffects embrace a rise in blood pressure, thrombosis and local injection website reactions. It has been associated with development of some tumours which express Epo receptors. These include metals such as iron and cobalt, vitamins (especially vitamin B12, folate, vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin B6, thiamine and riboflavin) and hormones such as androgens and thyroxine. In order to obtain this gaseous change they contain the specialized protein haemoglobin. Each molecule of regular adult haemoglobin A (Hb A) (the dominant haemoglobin in blood after the age of 3�6 months) consists of 4 polypeptide chains, 22, each with its personal haem group. Normal grownup blood additionally incorporates small portions of two different haemoglobins: Hb F and Hb A2. These also include chains, but with and chains, respectively, instead of (Table 2. The synthesis of the assorted globin chains in the fetus and adult is discussed in additional element in Chapter 7.
Zanaflex 2mg without a prescriptionInitial analysis Many genetic abnormalities are so specific for a specific illness that their presence determines that prognosis spasms 1983 trailer cheap zanaflex 2 mg visa. These approaches have an important function in determining the treatment of many forms of haemopoietic malignancy muscle relaxant drug test safe zanaflex 4mg. Inherited and environmental components each predispose to tumour improvement however the relative contribution of these is often unclear muscle relaxant drugs methocarbamol zanaflex 4 mg with amex. Infections (viral and bacterial) spasms right arm discount zanaflex 2 mg without prescription, medicine, radiation and chemical substances can all improve the risk of growing a haemopoietic malignancy. Haematological malignancies occur because of genetic alterations that lead to increased activation of oncogenes or decreased exercise of tumour suppressor genes. They often show about 10 acquired genetic mutations and progress in a linear or branching manner. These genetic alterations might occur through a wide range of mechanisms such as point mutation, chromosomal translocation or gene deletion. These investigations guide the prognosis, treatment and monitoring for residual illness of particular person circumstances. This has resulted from developments in supportive remedy and in particular treatment. Details of specific treatment are discussed in relation to particular person diseases within the acceptable chapter. Support care and common features of the agents used within the remedy of haematological malignancy are described right here. Up and about more than 50% of waking hours Capable of only limited selfcare, confined to bed or chair more than 50% of waking hours Completely disabled. Totally confined to bed or chair Dead 1 General assist therapy Patients with haematological malignancies often present with medical problems associated to suppression of regular haemopoiesis and this downside is compounded by the remedies that are given to eradicate the tumour. It can be necessary to examine for comorbidity corresponding to cardiac, pulmonary and renal disease. General supportive therapy for sufferers present process intensive treatment often contains the next. Insertion of a central venous catheter A central venous catheter is usually inserted for these patients who will want intensive remedy, and is completed by way of a skin tunnel from the chest into the superior vena cava. This gives ease of entry for administering chemotherapy, blood merchandise, antibiotics and intravenous feeding. Blood product assist (see Chapter 30) Red cell and platelet transfusions are used to deal with anaemia and thrombocytopenia. In patients needing each purple cells and platelets, platelets are given first to scale back the danger of an extra fall within the platelet count. Large volume transfusions, such as three units of blood or more, can precipitate pulmonary oedema in older sufferers and should be given slowly and with scientific monitoring. The trigger for platelet transfusion is often a platelet rely under 10 � 109/L but this ought to be doubled in the presence of energetic bleeding or an infection. The dosage of steroids must be restricted because of concerns with immunosuppression. The use of recombinant erythropoietin to scale back the necessity for blood transfusion and improve patient wellbeing. Tumour lysis syndrome Chemotherapy might trigger an acute rise in plasma uric acid, potassium and phosphate and cause hypocalcaemia because of fast lysis of tumour cells. This syndrome is seen most commonly with quickly dividing tumours corresponding to lymphoblastic lymphoma or acute leukaemia and can trigger acute renal failure. Allopurinol, intravenous fluids and electrolyte substitute are the mainstay of prevention and alkalinization of the urine is typically used. Rasburicase, an enzyme that oxidises uric acid to allantoin, is very effective in controlling hyperuricaemia. Psychological help Patients with a prognosis of malignant illness commonly feel concerns about such issues because the discomfort of remedy, finance, sexuality and fear of mortality. Psychological help must be an integral a half of the connection between physician and patient, and patients ought to be allowed to express their fears and issues at the earliest alternative. Most sufferers worth the opportunity to learn extra about their dysfunction and heaps of glorious booklets or websites at the moment are obtainable. Teamwork can additionally be essential and the nursing employees and trained counsellors have an important position in providing help and information throughout inpatient and outpatient care. Many units have specialist input from clinical psychologists and psychiatric assist could occasionally be required. Ethical issues regarding storage or potential utilization of tissue within the occasion of therapy failure might want to be addressed. Permanent infertility in women is less common after chemotherapy although premature menopause could occur. Storage of fertilized ova is usually impractical and specialist recommendation should be obtained in relation to storage of eggs. Cryoprecipitate or antithrombin could additionally be wanted for coagulation factor deficiency, such as that precipitated by asparaginase in the management of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Antiplatelet drugs similar to aspirin or clopidogrel are normally discontinued in patients undergoing intensive chemotherapy and patients on longterm warfarin could be switched to low molecular weight heparin, which can then itself be stopped if the platelet count falls below 50 � 109/L. Progesterones are given to premenopausal women undergoing intensive chemotherapy to prevent menstruation. Tranexamic acid could be given to cut back haemorrhage in patients with persistent lowgrade blood loss. If a weight loss of more than 10% happens, help with whole nutrition is commonly given, both enterally via a nasogastric tube or parenterally through a central venous catheter. The mucositis that follows intensive chemotherapy could cause severe discomfort and continuous infusions of opiate analgesia are sometimes required. Pain is commonly a considerable concern in patients with a number of myeloma and can be managed by a combination of analgesia and chemotherapy/radiotherapy. Advice from palliative care groups or specialist pain administration practitioners ought to be sought when required. Prophylaxis and remedy of infection Patients with haematological malignancy are at nice danger of infection which stays the most important cause of morbidity and mortality. Immunosuppression may outcome from neutropenia, hypogammaglobulinaemia and impaired mobile function. Neutropenia is a specific concern and in lots of sufferers neutrophils are totally absent from the blood for intervals of 2 weeks or more. Staphylococcus and Streptococcus) generally colonize central venous strains, whereas Gramnegative gut micro organism. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Proteus, Klebsiella and anaerobes) can cause overwhelming septicaemia.
Effective zanaflex 2mgIn the setting of hyperkalemia spasms cure buy generic zanaflex 2 mg on-line, the kidney is able to generating a major urinary excretion of K+ muscle relaxant drugs buy 2mg zanaflex free shipping. Drugs may be implicated in the genesis of hyperkalemia through a wide range of mechanisms muscle relaxant menstrual cramps buy generic zanaflex 4 mg. Heparin and ketoconazole can even contribute to hyperkalemia by way of the decreased manufacturing of aldosterone spasms coronary artery buy zanaflex 2mg on-line, though these agents alone are usually inadequate to maintain a clinically vital hyperkalemia. Severe hyperkalemia causes partial depolarization of the skeletal muscle cell membrane and will manifest as weak point, potentially progressing to flaccid paralysis and hypoventilation if the respiratory muscular tissues are involved. High aldosterone ranges, usually accompanied by excessive renin ranges, recommend aldosterone resistance (pseudohypoaldosteronism) but can be seen in K+-sparing diuretics. Acute remedy may encompass some or all the following (the hypokalemic effect is additive). Albuterol can be administered in a dose of 10-20 mg as a steady nebulized therapy over 30-60 minutes. This could be achieved with the administration of saline in patients who appear volume depleted. When given by mouth, the same old dose is 25-50 g combined with 100 mL 20% sorbitol to stop constipation. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate can be administered as a retention enema consisting of fifty g resin in one hundred fifty mL tap water. Enemas should be avoided in postoperative sufferers because of the increased incidence of colonic necrosis, especially following renal transplantation. Newer brokers similar to sodium zirconium cyclosilicate are being studied and have shown improved security profiles in preliminary research. Chronic remedy could involve dietary modifications to keep away from excessive K+ foods (see Potassium, Hyperkalemia, Etiology section), correction of metabolic acidosis with oral alkali, the promotion of kaliuresis with diuretics, and/or administration of exogenous mineralocorticoid in states of hypoaldosteronism. Nearly 50% of serum calcium is ionized (free), whereas the remainder is complexed to albumin (40%) and anions such as phosphate (10%). It stimulates intestinal absorption of calcium and is certainly one of many components that present feedback to the parathyroid gland. Underlying disturbances to calcium metabolism are thus often masked by compensatory mechanisms till the patient develops a P. Primary hyperparathyroidism causes most cases of hypercalcemia in ambulatory sufferers. It is a typical dysfunction, particularly in elderly ladies, in whom the annual incidence is approximately 2 in 1000. Nearly 85% of instances are because of an adenoma of a single gland, 15% to hyperplasia of all four glands, and 1% to parathyroid carcinoma. Malignancy is liable for most circumstances of hypercalcemia among hospitalized sufferers. Less common causes account for about 10% of cases of hypercalcemia: Increased vitamin D exercise happens with exogenous exposure to vitamin D or elevated generation of calcitriol in chronic granulomatous diseases. The milk-alkali syndrome describes the acute or chronic growth of hypercalcemia, alkalosis, and renal failure that will end result from the ingestion of enormous portions of calcium-containing antacids. Hyperthyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, extended immobilization, Paget disease, and acromegaly may be related to hypercalcemia. Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia is a rare, autosomal dominant dysfunction of the calcium-sensing receptor, which is characterised by asymptomatic hypercalcemia from childhood and a household history of hypercalcemia. If serum calcium rises above 13 mg/dL, renal failure with nephrocalcinosis and ectopic soft tissue calcifications are possible. Osteopenia and frequent fractures might happen from the disproportional resorption of bone in hyperparathyroidism. Rarely, osteitis fibrosa cystica can develop when hyperparathyroidism is profound and prolonged, resulting in "brown tumors" and marrow substitute. Diagnostic Testing the historical past and bodily examination ought to focus on (a) the period of signs of hypercalcemia, (b) clinical evidence of any of the unusual causes of hypercalcemia, and (c) symptoms and indicators of malignancy (which nearly always precede malignant hypercalcemia). If hypercalcemia has been current for greater than 6 months with out an apparent etiology, primary hyperparathyroidism is type of actually the trigger. Serum calcium ought to be interpreted with data of the serum albumin, or an ionized calcium should be measured. Serum phosphorus is commonly decreased in hyperparathyroidism as a result of stimulation of phosphaturia, whereas Paget disease and vitamin D intoxication each are probably to have increased phosphorus ranges. Urine calcium may be elevated in primary hyperparathyroidism as a end result of a filtered load of calcium that exceeds the capacity for renal reabsorption. If the family history and clinical picture are suggestive, sufferers with familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia can be distinguished from sufferers with major hyperparathyroidism by documenting a low calcium clearance by 24-hour urine assortment (<200 mg calcium per day) or fractional excretion of calcium (<1%). Maintenance fluids may be continued after achieving euvolemia to sustain a urine output of 100-150 mL/h. Loop diuretics can be utilized if indicators of volume overload restrict further saline administration while hypercalcemia persists. These agents cut back paracellular reabsorption of calcium within the loop of Henle and thus might slightly enhance calcium excretion. A hypocalcemic response is usually seen inside 2 days and may persist for two weeks or longer. Other options Calcitonin inhibits bone resorption and increases renal calcium excretion. Glucocorticoids are efficient in hypercalcemia due to hematologic malignancies and granulomatous manufacturing of calcitriol. After serum calcium stabilizes, the dose must be steadily decreased to the minimal needed to control symptoms of hypercalcemia. Toxicity (see Chapter 25, Arthritis and Rheumatologic Diseases) limits the usefulness of glucocorticoids for long-term therapy. It is given as a 100- to 200-mg/m2/d continuous infusion for as much as 5 days, until normocalcemia is achieved sooner. In many patients, this disorder has a benign course, with minimal fluctuation in serum calcium concentration and no apparent medical sequelae. Surgical intervention usually has a excessive success price (95%) with low morbidity and mortality. Management consists of liberal oral hydration with a high-salt diet, day by day bodily activity to reduce bone resorption, and avoidance of thiazide diuretics. Oral bisphosphonates and estrogen alternative remedy or raloxifene in postmenopausal girls can be considered in the appropriate clinical context. Bisphosphonate and glucocorticoid therapy with a calciumrestricted food plan (<400 mg/d) could be tried, though these maneuvers hardly ever yield longterm success except the malignancy responds to therapy. Denosumab may be utilized in patients with persistent hypercalcemia of malignancy in whom bisphosphonates may be contraindicated due to renal failure. Pseudohypocalcemia describes the state of affairs during which the whole calcium is reduced due to hypoalbuminemia, however the corrected [Ca2+] (see Calcium, Hypercalcemia, Diagnostic Testing section) and ionized calcium remain inside the regular ranges. In uncommon patients, hypoparathyroidism is congenital, as in DiGeorge syndrome or familial hypocalcemia.
Flavonoid (Hesperidin). Zanaflex. - Internal hemorrhoids, when used in combination with diosmin.
- Dosing considerations for Hesperidin.
- What is Hesperidin?
- How does Hesperidin work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Varicose veins and other conditions.
- Treating leg ulcers caused by poor circulation, when used in combination with diosmin.
- What other names is Hesperidin known by?
- Treating swelling of the arms following surgery for breast cancer.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96989
Order 2 mg zanaflexThe median nerve additionally innervates the thenar muscle tissue that are responsible for opposition of the thumb to the other digits spasms upper left abdomen order zanaflex 4 mg amex. The median nerve enters the hand by passing by way of the carpal tunnel and divides into a recurrent branch and palmar digital branches muscle relaxant m 751 trusted zanaflex 4mg. Originating from the lateral aspect of the median nerve close to the distal margin of the exor retinaculum spasms spasticity muscle zanaflex 2 mg fast delivery, it curves around the margin of the retinaculum and passes proximally over the exor pollicis brevis muscle infantile spasms 2 month old order zanaflex 2 mg without a prescription. The recurrent department then passes between the exor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis brevis to finish in the opponens pollicis. The palmar digital nerves cross the palm deep to the palmar aponeurosis and the super cial palmar arch and enter the digits. They innervate pores and skin on the palmar surfaces of the lateral three and one-half digits and cutaneous regions over the dorsal elements of the distal phalanges (nail beds) of the identical digits. Surface Anatomy Motor perform of the median and ulnar nerves in the hand the ability to ex the metacarpophalangeal joints whereas at the similar time extending the interphalangeal joints of the ngers is entirely depending on the intrinsic muscle tissue of the hand. These muscular tissues are mainly innervated by the deep department of the ulnar nerve, which carries bers from spinal cord degree (C8)T1. Adducting the ngers to grasp an object positioned between them is attributable to the palmar interossei muscular tissues, which are innervated by the deep department of the ulnar nerve carrying bers from spinal cord degree (C8)T1. The capacity to grasp an object between the pad of the thumb and the pad of one of the ngers is dependent upon regular functioning of the thenar muscle tissue, which are innervated by the recurrent branch of the median nerve carrying bers from spinal twine stage C8(T1). Super cial branch of the radial nerve the one a half of the radial nerve that enters the hand is the tremendous cial branch. It enters the hand by passing over the anatomical snuffbox on the dorsolateral side of the wrist. Anatomical s nuffbox Superficial department (of radial nerve) Palm ar view Dorsal view. The most common radial nerve harm is damage to the nerve in the radial groove of the humerus, which produces a global paralysis of the muscular tissues of the posterior compartment leading to "wrist drop. The typical damage produces discount of sensation within the cutaneous distribution, predominantly over the posterior aspect of the hand. Severing the posterior interosseous nerve (continuation of deep department of radial nerve) might paralyze the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm, however the nerve provide is variable. The distal branches of the super cial branch of the radial nerve may be readily palpated as "cords" passing over the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus within the anatomical snuffbox. Damage to these branches is of little consequence as a result of they supply solely a small area of pores and skin. Abduction and adduction of the index, center, and ring ngers is controlled predominantly by T1. C3 C4 T2 C5 C5 C3 C4 T2 C5 T1 T1 C6 C6 C8 C6 C7 C7 T1 Clinical app Dermatomes and myotomes in the higher limb Innervation of the upper limb is by the brachial plexus, which is formed by the anterior rami of cervical spinal nerves C5 to C8, and T1. This plexus is initially fashioned within the neck after which continues into the upper limb. Major nerves that ultimately innervate the arm, forearm, and hand originate from the brachial plexus. As a consequence of this innervation sample, medical testing of lower cervical and T1 nerves is carried out by analyzing dermatomes, myotomes, and tendon re exes in the higher limb. Another consequence is that the clinical signs of problems related to lower cervical nerves-pain, pins and needles sensations or paresthesia, and muscle twitching-appear within the upper limb. Importantly, the main spinal cord degree related to innervation of the diaphragm, C4, is immediately above the spinal wire ranges related to the higher limb. Evaluation of dermatomes and myotomes in the higher limb can present essential information about potential respiratory issues which may develop as complications of injury to the spinal wire in regions just under the C4 spinal stage. Clinical app Tendon faucets in the upper limb In an unconscious affected person, both somatic sensory and motor capabilities of spinal twine levels could be examined using tendon re exes: A faucet on the tendon of the biceps in the cubital fossa tests primarily for spinal twine level C6. Sensation in these areas can be used to test for peripheral nerve lesions: the axillary nerve innervates pores and skin on the superior lateral floor on the arm. Anterior the musculocutaneous nerve innervates skin on the anterolateral side of the forearm. The median nerve innervates the palmar surface of the lateral three and one-half digits. The radial nerve provides skin on the posterior floor of the forearm and the dorsolateral surface of the hand. Posterior Axillary ne rve � Superior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm Axillary ne rve � Superior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm Radial ne rve � Inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm T2 Radial ne rve � Inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm � Pos terior cutaneous nerve of arm � Pos terior cutaneous nerve of forearm T2 Mus c ulo c utane o us ne rve � Lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm T1 Mus c ulo c utane o us ne rve � Lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm Radial ne rve � Superficial branch T1 Radial ne rve � Superficial branch Ulnar ne rve Ulnar ne rve Me dian ne rve Me dian ne rve. Brachial pulse in midarm: brachial artery on the medial aspect of the arm within the cleft between the biceps brachii and triceps brachii muscular tissues. Brachial pulse within the cubital fossa: brachial artery medial to the tendon of the biceps brachii muscle. This is the position the place a stethoscope is placed to hear the pulse of the vessel when taking a blood stress studying. Radial pulse in the distal forearm: radial artery instantly lateral to the tendon of the exor carpi radialis muscle. Radial pulse within the anatomical snuffbox: radial artery as it crosses the lateral side of the wrist between the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle and the tendons of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus muscles. The head consists of a collection of compartments, that are shaped by bone and soft tissues. They are: the cranial cavity, two ears, two orbits, two nasal cavities, and an oral cavity. The visceral compartment incorporates essential glands (thyroid, parathyroid, and thymus), and elements of the respiratory and digestive tracts (larynx and pharynx) that pass between the pinnacle and thorax. The two vascular compartments, one on each side, contain the major blood vessels and the vagus nerve. Mus culofas cial collar (Inves ting fas cia) Anterior Vis ceral compartment Vas cular compartment Vertebral compartment Posterior. Contains the upper parts of the respiratory and digestive systems-the nasal and oral cavities-which have structural features for modifying the air or food passing into every system. The cranium may be subdivided into: an upper domed half (the calvaria), which covers the cranial cavity containing the mind; a base that consists of the oor of the cranial cavity; and a decrease anterior part-the facial skeleton (viscerocranium). The bones forming the calvaria are mainly the paired temporal and parietal bones, and parts of the unpaired frontal, sphenoid, and occipital bones. The bones forming the base of the skull are mainly parts of the sphenoid, temporal, and occipital bones. The bones forming the facial skeleton are the paired nasal bones, palatine bones, lacrimal bones, zygomatic bones, maxillae, inferior nasal conchae, and the unpaired vomer. Importantly, it permits an individual to position sensory systems in the head relative to environmental cues with out transferring the complete body. Contains specialized buildings (pharynx and larynx) that connect the upper components of the digestive and respiratory tracts (nasal and oral cavities) in the head, with the esophagus and trachea, which start relatively low within the neck and cross into the thorax.
Zanaflex: 4 mg, 2 mg
Trusted zanaflex 4mgBecause the reaction that ensues is mediated largely by histamine muscle spasms 2 weeks buy 4 mg zanaflex visa, antihistamines can attenuate this response and are the mainstay of therapy quetiapine spasms order zanaflex 2 mg with amex. Atopic dermatitis (commonly referred to as eczema) is a part of the atopic triad (atopic dermatitis muscle relaxer jokes zanaflex 2mg, allergic rhinitis gas spasms in stomach order zanaflex 2 mg mastercard, and asthma) but also can happen in isolation. It is a typical skin disorder, usually related to filaggrin mutations, resulting in defective pores and skin barrier operate. Some patients with atopic dermatitis develop asthma, a sequence that clinicians discuss with as the "atopic march. This assumption is supported by the correlation of some infections with elevated IgE levels and eosinophilia. Studies in mice that had been poor in IgE, Th2 cytokines, or mast cells have offered evidence that IgE- and mast cell�mediated responses are necessary for protection in opposition to certain forms of infection. IgE-initiated immune reactions may contribute to the eradication of assorted microbes, together with helminthic parasites. Eosinophil-mediated killing of helminths is an effective defense towards these organisms (see Chapter 10). In addition, IgE-dependent mast cell activation in the gastrointestinal tract promotes the expulsion of parasites by rising peristalsis and by an outpouring of mucus. Furthermore, genetically mast cell�deficient mice present increased susceptibility to an infection by tick larvae, and immunity may be offered to these mice by adoptive switch of specific IgE and mast cells (but not by either element alone). Nonetheless, the position of type 2 responses in protecting people from helminths is controversial, and human worm infections are regularly sustained for many years within the face of persistent Type 2 responses. Mast cells play an necessary protecting function as part of the innate immune response to bacterial infections and venoms. Studies in mice have indicated that mast cells can be activated by IgE-independent mechanisms in the center of an acute bacterial infection and that the mediators they release are important for clearing the infection. Mast cell�deficient mice are much less able to clearing and are more doubtless to die of acute bacterial infection of the peritoneum than are regular mice. Several empirical immunotherapy protocols have been used, which induce a number of immunologic alterations that may account for the scientific benefit. In one method, referred to as desensitization, or particular immunotherapy, or "allergy vaccines," small quantities of antigen are repeatedly administered subcutaneously. As a results of this therapy, particular IgE levels decrease and IgG titers usually rise, perhaps additional inhibiting IgE manufacturing by neutralizing the antigen and by antibody feedback (see Chapter 12). The helpful effects of desensitization may occur in a matter of hours, a lot earlier than changes in IgE levels. Although many individuals with extra common continual atopic situations, such as hay fever and asthma, profit from desensitization therapy, the overall effectiveness for allergic problems is more variable. It is now possible to identify the allergens that bind to IgE in each affected person, using chip-based antibody-binding assays, and this may greatly facilitate the development of antigen-specific immunotherapy. Feeding youngsters small amounts of peanut-containing meals from a very young age reduces the event of peanut allergy later in life. This latest finding has 456 Chapter 20 � Allergy mast cells, and complement activation by the alternative pathway, resulting in the release of C5a, which instantly triggers mast cell degranulation. It can be potential that the classical pathway of complement might be activated by natural antibodies which may be produced by B-1 cells and that acknowledge frequent microbial pathogens. Mast cell�derived proteases have been proven to destroy some snake and insect venoms in mice, and venom-specific IgE confers protection from envenomation. This is an uncommon type of innate immunity against a probably deadly encounter with nonmicrobial organisms and their toxins. The steps in the growth of immediate hypersensitivity are publicity to an antigen (allergen) that stimulates Th2 responses and IgE production, binding of the IgE to Fc receptors on mast cells, cross-linking of the IgE and the Fc receptors by the allergen, activation of mast cells, and release of mediators. Subsets of mast cells, together with mucosal and connective tissue mast cells, may produce completely different mediators. Basophils are a type of circulating granulocyte that expresses highaffinity Fc receptors and accommodates granules with contents similar to these of mast cells. On binding of antigen to IgE on the floor of mast cells or basophils, the high-affinity Fc receptors become cross-linked and activate intracellular second messengers that lead to granule release and new synthesis of mediators. Y Y rapid vascular and clean muscle reactions of quick hypersensitivity, corresponding to vasodilation, vascular leakage and edema, bronchoconstriction, and gut hypermotility. Cytokines released by mast cells and Th2 cells mediate the late-phase reaction, which is an inflammatory reaction involving neutrophil and eosinophil infiltration. Susceptibly to allergic diseases is inherited, and allelic variations of a number of genes have been related to allergic bronchial asthma. Various organs show distinct types of immediate hypersensitivity involving completely different mediators and target cell varieties. Asthma is a manifestation of instant hypersensitivity and late-phase reactions within the lung. Allergic rhinitis (hay fever) is the commonest allergic illness of the higher respiratory tract. In the skin, instant hypersensitivity is manifested as wheal-andflare and late-phase reactions and will lead to continual eczema. Drug therapy is geared toward inhibiting mast cell mediator manufacturing and at blocking or counteracting the consequences of launched mediators on track organs. The goal of immunotherapy is to prevent or reduce Th2 cell responses to particular allergens and the manufacturing of IgE. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions present safety towards helminthic infections by promoting IgE- and eosinophil-mediated antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and gut peristalsis. Mast cells may also play a task in innate immune responses to bacterial infections. Asthma as a persistent disease of the innate and adaptive immune techniques responding to viruses and allergens. This chapter describes the major types of congenital and bought immunodeficiencies, with an emphasis on their pathogenesis and the elements of the immune system that are involved in these issues. The principal consequence of immunodeficiency is increased susceptibility to an infection. Deficient humoral immunity normally ends in an infection by encapsulated, pus-forming micro organism and some viruses, whereas defects in cell-mediated immunity result in infection by viruses and different intracellular microbes or the reactivation of latent infections. Combined deficiencies in both humoral and cell-mediated immunity make patients susceptible to an infection by all courses of microorganisms. Immunodeficient sufferers, particularly these with defects in mobile immunity, typically current with infections by microbes which are generally encountered however effectively eliminated by wholesome persons; such infections are stated to be opportunistic. Defects in innate immunity may end up in infections by completely different classes of microbes, relying on the pathway or cell kind affected. There is rising proof that adults with recurrent or severe infections usually harbor mutations in genes that regulate immune operate. Defects in a number of elements of the immune system can lead to critical and sometimes deadly disorders, which are collectively known as immunodeficiency ailments.

Generic zanaflex 2 mg visaSuprascapular artery the suprascapular artery originates within the base of the neck as a branch of the thyrocervical trunk muscle relaxant hair loss generic zanaflex 2 mg without prescription, which in turn muscle relaxant histamine release cheap 2 mg zanaflex free shipping, is a serious department of the subclavian artery back spasms 6 weeks pregnant purchase zanaflex 4 mg with visa. The vessel can also originate instantly from the third a part of the subclavian artery muscle relaxant drugs for neck pain order 2 mg zanaflex with visa. The suprascapular artery normally enters the posterior scapular region superior to the suprascapular foramen, whereas the nerve passes through the foramen. Because this area is under the inferior margin of the teres major, which de nes the inferior boundary of the axilla, the triangular interval serves as a passageway between the anterior and posterior compartments of the arm and between the posterior compartment of the arm and the axilla. The radial nerve, the profunda brachii artery (deep artery of arm), and associated veins cross by way of it. Suprascapular nerve the suprascapular nerve originates within the base of the neck from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus. It passes posterolaterally from its origin, by way of the suprascapular foramen to attain the posterior scapular area, the place it lies in the plane between bone and muscle. It innervates the supraspinatus muscle, then passes by way of the greater scapular (spinoglenoid) notch, between the basis of the spine of the scapula and the glenoid cavity, to terminate in and innervate the infraspinatus muscle. Regional anatomy � Axilla Ante rio r wall � Pectoralis major and minor mus cles � Subclavius mus cle � Clavipectoral fas cia Late ral wall � Intertubercular s ulcus Inle t � Lateral margin of rib I � Clavicle � Superior margin of s capula to coracoid proces s Axillary s heath s urrounding arteries, veins, nerves, and lymphatics Me dial wall � Upper thoracic wall � Serratus anterior mus cle Flo o r � Skin of armpit � Open laterally into arm Axilla Apex of inlet Inlet 7 Middle s calene mus cle Anterior s calene mus cle Lateral margin of rib I Clavicle Coracoid proces s Medial wall Lateral wall Anterior wall Pos terior wall Skin Po s the rio r wall � Subs capularis, teres main and latis s imus dors i mus cles, and long head of triceps B brachii mus cle Skin on floor of axilla Skin of arm A C. In addition to supplying the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscle tissue, the suprascapular artery contributes branches to numerous buildings along its course. Formed by the clavicle, the scapula, the upper thoracic wall, the humerus, and related muscle tissue, the axilla is an irregularly shaped pyramidal house with. The axillary inlet is continuous superiorly with the neck, and the lateral part of the oor opens into the arm. All main structures passing into and out of the upper limb move through the axilla. Apertures fashioned between muscle tissue in the anterior and posterior partitions allow buildings to move between the axilla and immediately adjoining regions (the posterior scapular, pectoral, and deltoid regions). Posterior circum ex humeral artery the posterior circum ex humeral artery originates from the third part of the axillary artery in the axilla. The posterior circum ex humeral artery and axillary nerve depart the axilla by way of the quadrangular house within the posterior wall and enter the posterior scapular area. Circum ex scapular artery the circum ex scapular artery is a department of the subscapular artery that also originates from the third part of the axillary artery within the axilla. The circum ex scapular artery leaves the axilla via the triangular house and enters the posterior scapular area, passes through the origin of the teres minor muscle, and types anastomotic connections with other arteries within the area. Axillary inlet the axillary inlet is oriented within the horizontal airplane and is considerably triangular in form, with its apex directed laterally. The margins of the inlet are utterly formed by bone: the medial margin is the lateral border of rib I. The posterior margin is the superior border of the scapula as a lot as the coracoid process. Veins Veins in the posterior scapular area generally comply with the arteries and join with vessels within the neck, again, arm, and axilla. Major vessels and nerves move between the neck and the axilla by crossing over the lateral border of rib I and thru the axillary inlet. The subclavian artery, the most important blood vessel supplying the higher limb, turns into the axillary artery as it crosses the lateral margin of rib I and enters the axilla. Similarly, the axillary vein becomes the subclavian vein because it passes over the lateral margin of rib I and leaves the axilla to enter the neck. At the axillary inlet, the axillary vein is anterior to the axillary artery, which, in turn, is anterior to the trunks of the brachial plexus. As they pass over rib I, the vein and artery are separated by the insertion of the anterior scalene muscle. Anterior wall the anterior wall of the axilla is shaped by the lateral a part of the pectoralis major muscle, the underlying pectoralis minor and subclavius muscle tissue, and the clavipectoral fascia (Table 7. Regional anatomy � Axilla the medial pectoral nerve leaves the axilla by penetrating instantly through the pectoralis minor muscle to supply this muscle and to reach the pectoralis major muscle. Occasionally, branches of the medial pectoral nerve move across the lower margin of the pectoralis minor to attain and innervate the overlying pectoralis main muscle. It encloses the subclavius and pectoralis minor muscular tissues and spans the hole between them. Structures journey between the axilla and the anterior wall of the axilla by passing via the clavipectoral fascia either between the pectoralis minor and subclavius muscles or inferior to the pectoralis minor muscle. Important constructions that move between the subclavius and pectoralis minor muscle tissue embrace the cephalic vein, the thoraco-acromial artery, and the lateral pectoral nerve. The lateral thoracic artery leaves the axilla by passing through the fascia inferior to the pectoralis minor muscle. Medial wall the medial wall of the axilla consists of the upper thoracic wall (the ribs and associated intercostal tissues) and the serratus anterior muscle (Table 7. The only main structure that passes instantly through the medial wall and into the axilla is the intercostobrachial nerve. It communicates with a branch of the brachial plexus (the medial cutaneous nerve of the arm) within the axilla and supplies skin on the higher posteromedial side of the arm, which is a half of the T2 dermatome. Loss of perform of this muscle causes the medial border, and significantly the inferior angle, of the scapula to elevate away from the thoracic wall, leading to characteristic "winging" of the scapula, on pushing ahead with the arm. Intertubercular s ulcus Pectoralis main Teres major Lateral wall the lateral wall of the axilla is slender and fashioned totally by the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus. The pectoralis major muscle of the anterior wall attaches to the lateral lip of the intertubercular sulcus. The latissimus dorsi and teres main muscles of the posterior wall connect to the oor and medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus, respectively (Table 7. Latis s imus dors i Posterior wall the posterior wall of the axilla is complex (Table 7. Gaps between the muscular tissues of the posterior wall kind apertures via which structures cross between the axilla, posterior scapular region, and posterior compartment of the arm. Together with three muscular tissues of the posterior scapular area (the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor muscles), the subscapularis is a member of the rotator cuff muscular tissues, which stabilize the glenohumeral joint. The lengthy head of the triceps brachii muscle passes vertically via the posterior wall of the axilla, and, along with surrounding muscle tissue and adjacent bones, results in the formation of three apertures via which main structures cross by way of the posterior wall. Passing via the quadrangular area are the axillary nerve and the posterior circum ex humeral artery and vein. The radial nerve passes out of the axilla traveling through this interval to attain the posterior compartment of the arm. Gateways within the posterior wall (See additionally "Gateways to the posterior scapular area," p. When considered from anteriorly, its boundaries are fashioned by: the inferior margin of the subscapularis muscle; the surgical neck of the humerus; Floor the oor of the axilla. The subclavian artery within the neck becomes the axillary artery at the lateral margin of rib I and passes through the axilla, changing into the brachial artery at the inferior margin of the teres main muscle. The axillary artery is separated into three parts by the pectoralis minor muscle, which crosses anteriorly to the vessel. Two branches, the thoracoacromial artery and the lateral thoracic artery, originate from the second part.
Zanaflex 4 mg lineThe platelet depend is usually reasonably raised in iron deficiency muscle relaxant drugs flexeril 4mg zanaflex with amex, particularly when haemorrhage is constant spasms spinal cord injury generic 4 mg zanaflex with mastercard. In iron deficiency anaemia the serum ferritin could be very low whereas a raised serum ferritin indicates iron overload or excess release of ferritin from damaged tissues or an acute section response spasms calf muscles cheap zanaflex 2 mg fast delivery. In men and postmenopausal girls spasms going to sleep order zanaflex 2 mg on line, fuel trointestinal blood loss is the primary cause of iron deficiency and the precise site is sought from the clinical historical past, bodily and rectal examination, by occult blood tests, and by acceptable use of higher and decrease gastrointestinal endoscopy and/or radi ology. Tests for parietal cell antibodies, Helicobacter infec tion and serum gastrin level could assist to diagnose autoimmune gastritis. In tough circumstances a digicam in a capsule could be swal lowed which relays footage of the gastrointestinal tract elec tronically. Tests for transglutaminase antibodies and duodenal biopsy to look for gluteninduced enteropathy could be useful. Hookworm ova are sought in stools of topics from areas the place this infestation happens. Two populations of pink cells are current: one microcytic and hypochromic, the other normocytic and nicely haemoglobinized. Serum ferritin A small fraction of physique ferritin circulates in the serum, the focus being related to tissue, particularly reticulo endothelial, iron shops. In some laboratories, the transferrin content material of serum is measured instantly by immunodiffusion, quite than by its ability to bind iron, and is expressed in g/L. Normal serum accommodates 2�4 g/L transferrin (1 g/L transferrin = 20 mol/L binding capacity). Oral iron the most effective preparation is ferrous sulphate which is cheap, con tains 67 mg iron in each 200mg tablet and is finest given on an empty abdomen in doses spaced by no much less than 6 hours. Continuing haemorrhage Failure to take tablets Wrong analysis � particularly thalassaemia trait, sideroblastic anaemia Mixed deficiency � associated folate or vitamin B12 deficiency Another cause for anaemia. Intra venous iron has also been found to improve useful capac ity and high quality of life in some patients with congestive coronary heart failure, even within the absence of anaemia (see p. There could additionally be a haematologi cal response to intravenous but often not to oral iron. Oral iron remedy ought to be given for lengthy sufficient both to right the anaemia and to replenish body iron stores, which often means for a minimal of 6 months. Iron for tification of the food plan in infants in Africa reduces the incidence of anaemia but will increase suceptibility to malaria. Parenteral iron Many different preparations can be found with various licens ing in numerous countries. Iron dextran (CosmoFer) may be given as sluggish intravenous injection or infusion both in small single doses or as a complete dose infusion given in 1 day. Ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject) and ferric isomaltoside (Monofer) may also be given as a complete dose in 1 day by sluggish intravenous infusion. Ferric hydroxide�sucrose (Venofer) is administered by gradual intravenous injection or infusion, to a maximum of 200 mg iron in each infusion. There could additionally be hypersensitivity or anaphylactoid reactions to parenteral iron, particularly in these with a previous reaction, a quantity of drug allergies and extreme atopy. Parenteral iron is given slowly and solely when there are excessive iron requirements as in gastrointestinal bleeding, extreme males orrhagia, continual haemodialysis, with erythropoietin remedy, and when oral iron is ineffective. In many conditions this anaemia is complicated by anaemia resulting from other causes. Sideroblastic anaemia this is a refractory anaemia defined by the presence of many pathological ring sideroblasts within the bone marrow. Sideroblastic anaemia is diagnosed when 15% or more of marrow erythroblasts are ring sideroblasts. In the hereditary forms the anaemia is normally character ized by a markedly hypochromic and microcytic blood image. Other rare sorts include an Xlinked disease with spinocerebellar degeneration and ataxia, mitochondrial defects. The much more frequent form is refractory anaemia with ring sideroblasts, which is a subtype of myelodysplasia (see Chapter 16). In many severe cases, however, repeated blood transfusions are the one methodology of maintain ing a passable haemoglobin concentration, and transfusional Chapter 3: Hypochromic anaemias / 39 Table 3. Ring sideroblast formation (<15% of erythroblasts) can also occur in the bone marrow in: other malignant diseases of the marrow. Lead poisoning Lead inhibits each haem and globin synthesis at a number of points. The anaemia could additionally be hypochromic or predominantly haemolytic, and the bone marrow may show ring sideroblasts. The medical history is particularly important because the supply of the haemorrhage leading to iron deficiency or the presence of a persistent illness may be revealed. The nation of origin and the household historical past could counsel a potential diagnosis of thalassae mia or different genetic defect of haemoglobin. Physical examina tion can also be helpful in determining a website of haemorrhage, features of a chronic inflammatory or malignant illness, koilo nychia or, in some haemoglobinopathies, an enlarged spleen or bony deformities. Con versely, in iron deficiency anaemia the indices fall progres sively with the diploma of anaemia and when anaemia is mild the indices are regular or only just reduced beneath normal. Iron deficiency or the anaemia of persistent disor ders may also happen in these subjects. Hepcidin is the main regulator of iron absorption and iron launch from macrophages. Iron metabolism is regulated according to iron standing by intracellular iron regulatory proteins and by management of hepcidin synthesis. The serum ferritin, serum iron and saturation of the ironbinding capability are decreased. Dietary consumption is essential significantly in underdeveloped countries where hookworm and schistosomiasis are additionally important causes of blood loss. It is handled by oral or parenteral iron and by treating, so far as potential, the underlying trigger. Other frequent causes of a hypochromic, microcytic anaemia are the anaemia of chronic disorders, which happens in sufferers with persistent inflammatory or malignant ailments, and or thalassaemia. Less frequent causes embody sideroblastic anaemia (some cases) and lead poisoning. Iron overload (haemosiderosis) happens in problems associated with extreme absorption or in sufferers with extreme refractory anaemias who receive regular blood transfusion. Excessive iron deposition in tissues might end in severe harm to organs, notably the center, liver and endocrine organs. Increased iron absorption Hereditary (primary) haemochromatosis Ineffective erythropoiesis. The percentage saturation of transferrin (which is a measure of ironbinding capacity) is also valuable.

Zanaflex 2 mg discountTreatment is with embolization muscle relaxant injection for back pain purchase 4mg zanaflex fast delivery, laser therapy spasms constipation zanaflex 2 mg lowest price, oestrogens muscle relaxant for stiff neck order 4 mg zanaflex with visa, tranexamic acid and iron supplementation back spasms 20 weeks pregnant order zanaflex 4 mg on line. Thalidomide, lenalinomide and bevcizumab (antivascular endothelial growth factor) have been use to try to scale back gastrointestinal bleeding in severe instances. Connective tissue disorders In the Ehlers�Danlos syndromes there are hereditary collagen abnormalities with purpura ensuing from defective platelet adhesion, hyperextensibility of joints and hyperelastic friable pores and skin. Patients may current with superficial bruising and purpura following minor trauma or after the appliance of a tourniquet. Acquired vascular defects 1 Simple simple bruising is a standard benign disorder which happens in otherwise healthy girls, particularly those of childbearing age. Vascular bleeding problems the vascular problems are a heterogeneous group of situations characterised by simple bruising and spontaneous bleeding from the small vessels. Platelets/vessel wall illnesses Mucosal bleeding Petechiae Deep haematomas Bleeding from skin cuts Sex of affected person Common Common Rare Persistent Equal Coagulation illnesses Rare Rare Characteristic Minimal >80% male Table 25. Grade zero Grade 1 Grade 2 None Petechiae, ecchymoses, occult blood loss, gentle spotting Gross bleeding, i. The attribute purpuric rash accompanied by localized oedema and itching is usually most outstanding on the buttocks and extensor surfaces of the lower legs and elbows. It is normally a selflimiting situation but occasional patients develop renal failure. In vitamin C deficiency faulty collagen could trigger perifollicular petechiae, bruising and mucosal haemorrhage. Tranexamic acid and aminocaproic acid are helpful anti fibrinolytic medicine which will scale back bleeding ensuing from vascular issues or thrombocytopenia, but are comparatively contraindicated in the presence of haematuria because they may lead to clots obstructing the renal tract. Chapter 25: Bleeding problems / 281 Thrombocytopenia Abnormal bleeding related to thrombocytopenia or irregular platelet operate is characterised by spontaneous pores and skin purpura. Failure of platelet manufacturing this is the most typical reason for thrombocytopenia and is often part of a generalized bone marrow failure (Table 25. Selective megakaryocyte depression could end result from drug toxicity or viral infection. Failure of platelet manufacturing Selective megakaryocyte melancholy rare congenital defects (see text) drugs, chemical compounds, viral infections Part of basic bone marrow failure cytotoxic medicine radiotherapy aplastic anaemia leukaemia myelodysplastic syndromes myelofibrosis marrow infiltration. Diagnosis of those causes of thrombocytopenia is created from the medical history, peripheral blood depend, the blood movie and bone marrow examination. Bone marrow suppression Predictable (doserelated) ionizing radiation, cytotoxic medication, ethanol Occasional chloramphenicol, cotrimoxazole, idoxuridine, penicillamine, organic arsenicals, benzene, and so forth. The highest incidence has been thought-about to be in women aged 15�50 years, though some stories recommend an increasing incidence with age. Pathogenesis Platelet autoantibodies, normally IgG, outcome in the premature removing of platelets from the circulation by macrophages of the reticuloendothelial system, especially the spleen. Total megakaryocyte mass and platelet turnover are increased in parallel to roughly five occasions normal. Clinical options the onset is usually insidious with petechial haemorrhage, simple bruising and, in ladies, menorrhagia. These are orally lively or given by injection and act to increase platelet manufacturing. Treatment 6 7 As it is a chronic disease the purpose of remedy ought to be to keep a platelet count above the level at which spontaneous bruising or bleeding happens with the minimal of intervention. Prednisolone 1 mg/kg/day is the identical old initial remedy in adults and the dosage is steadily reduced after 10�14 days. In poor responders the dosage is reduced extra slowly however alternative immunosuppression or splenectomy is taken into account. The mechanism of action may be blockage of Fc receptors on macrophages or modification of autoantibody production. Trials of their use as initial remedy in combination with corticosteroids are in progress. Increased reticulin and fibrosis within the bone marrow may happen with prolonged therapy however are reversible on stopping the remedy. Other treatments that may elicit a remission embrace danazol (an androgen which may trigger virilization in women) and intravenous antiD immunoglobulin. Helicobacter pylori infection ought to be treated as there are some stories that this will likely improve the platelet rely, particularly in nations the place the incidence of the an infection is widespread. Platelet transfusions Platelet concentrates are useful in sufferers with acute lifethreatening bleeding however their profit will only last for a few hours. In approximately 75% of patients the episode follows vaccination or an infection corresponding to chickenpox or infectious mononucleosis. Spontaneous remissions are usual however in 5�10% of cases the illness becomes continual, lasting greater than 6 months. If the platelet rely is over 30 � 109/L no remedy is necessary until the bleeding is severe. Infections It seems doubtless that the thrombocytopenia associated with many viral and protozoal infections is immunemediated. Druginduced immune thrombocytopenia An immunological mechanism has been demonstrated as the cause of many druginduced thrombocytopenias. Quinine (including that in tonic water), quinidine and heparin are notably common causes (Table 25. The platelet count is usually less than 10 � 109/L, and the bone marrow exhibits regular or increased numbers of megakaryocytes. Drugdependent antibodies against platelets may be demonstrated within the sera of some patients. The quick remedy is to cease all suspected medicine however platelet concentrates ought to be given to sufferers with dangerous bleeding. If complement is hooked up and the sequence goes to completion, the platelet may be lysed directly. These strings are capable of embolizing to microvessels downstream and contributing to organ ischemia. The microvascular thrombosis causes variable levels of tissue ischaemia and infarction and is responsible for the microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia and thrombocytopenia. In refractory circumstances and continual relapsing circumstances, excessive dose corticosteroids, vincristine, intravenous immunoglobulin, rituximab and immunosuppressive therapy with azathioprine or cyclophosphamide have been used. Many cases are associated with Escherichia coli an infection with the verotoxin 0157 pressure or with other organisms, particularly Shigella. Supportive renal dialysis and management of hypertension are the mainstays of therapy. Chapter 25: Bleeding problems / 287 Disseminated intravascular coagulation In this disorder thrombocytopenia may end result from a high fee of platelet destruction due to elevated ranges of consumption. In splenomegaly, up to 90% of platelets could additionally be sequestered within the spleen, whereas normally this accounts for approximately onethird of the total platelet mass. Massive transfusion syndrome Platelets are unstable in blood stored at 4�C and the platelet rely quickly falls in blood saved for greater than 24 hours. Patients transfused with huge quantities of stored blood, corresponding to more than 10 models over a 24hour interval, frequently show abnormal clotting and thrombocytopenia.
References - Hiratzka LF, Eagle KA, Liang L, et al: Atherosclerosis secondary prevention performance measures after coronary bypass graft surgery compared with percutaneous catheter intervention and nonintervention patients in the Get With the Guidelines database, Circulation 116(Suppl 11): I207-I212, 2007.
- Szabo L, Fegyverneki S: Maximum and average urine flow rates in normal children?the Miskolc nomograms, Br J Urol 76(1):16-20, 1995.
- Creasey GH, Grill JH, Korsten M, et al: An implantable neuroprosthesis for restoring bladder and bowel control to patients with spinal cord injuries: a multicenter trial, Arch Phys Med Rehabil 82(11):1512n1519, 2001.
- American Diabetes Association: Tests of glycemia in diabetes, Diabetes Care 26:106-108, 2003.
- Traish AM, Guay AT: Are androgens critical for penile erections in humans? Examining the clinical and preclinical evidence, J Sex Med 3:382n404, discussion 404n387, 2006.
- Kunik ME, Veazey C, Cully JA, et al. COPD education and cognitive behavioral therapy group treatment for clinically significant symptoms of depression and anxiety in COPD patients: a randomized controlled trial. Psychol Med 2008; 38: 385-396.
- Lubanski MS, McCullough PA. Kidney's role in hypertension. Minerva Cardioangiol 2009;57(6):743-759.
- Yokomine K, Senju S, Nakatsura T, et al. The forkhead box M1 transcription factor as a candidate of target for anti-cancer immunotherapy. Int J Cancer. 2010;126:2153-2163.
|